Panobinostat
Panobinostat also called Farydak or LBH589, is a cancer drug used in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone to treat refractory or relapsed multiple myeloma after at least 2 other types of treatment have been tried. Panobinostat is usually given after other cancer medicines have been tried without success. Panobinostat is used in patients who have already been treated with bortezomib and an immunomodulating agent. Panobinostat is in a class of medications called histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors and a type of antiangiogenesis agent. Panobinostat blocks certain enzymes needed for cells to grow and divide and may kill cancer cells. Panobinostat may also prevent the growth of new blood vessels that tumors need to grow. Panobinostat is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer.
Panobinostat is an oral small molecule inhibitor of histone deacetylases (HDAC) , thereby preventing removal of acetyl groups from histones. The accumulation of acetyl groups on histones causes cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death. Malignant cells are particularly sensitive to the effects of inhibition of histone deacetylases. In open label studies in patients with multiple myeloma, panobinostat in combination with bortezomib (a proteasome inhibitor) yielded overall response rates of up to 50% and some responders had long term remissions. A large, controlled trial in patients with advanced, refractory multiple myeloma demonstrated prolongation of progression-free survival by the addition of panobinostat to bortezomib and dexamethasone, but the overall survival was not different at the time of the initial analysis.
Panobinostat was approved in 2015 by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on an “accelerated” basis 1 to be used in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone in patients with refractory or relapsed multiple myeloma. In clinical studies, Panobinostat slowed progression of multiple myeloma. However, it has not been shown that panobinostat can improve symptoms or lengthen survival time.
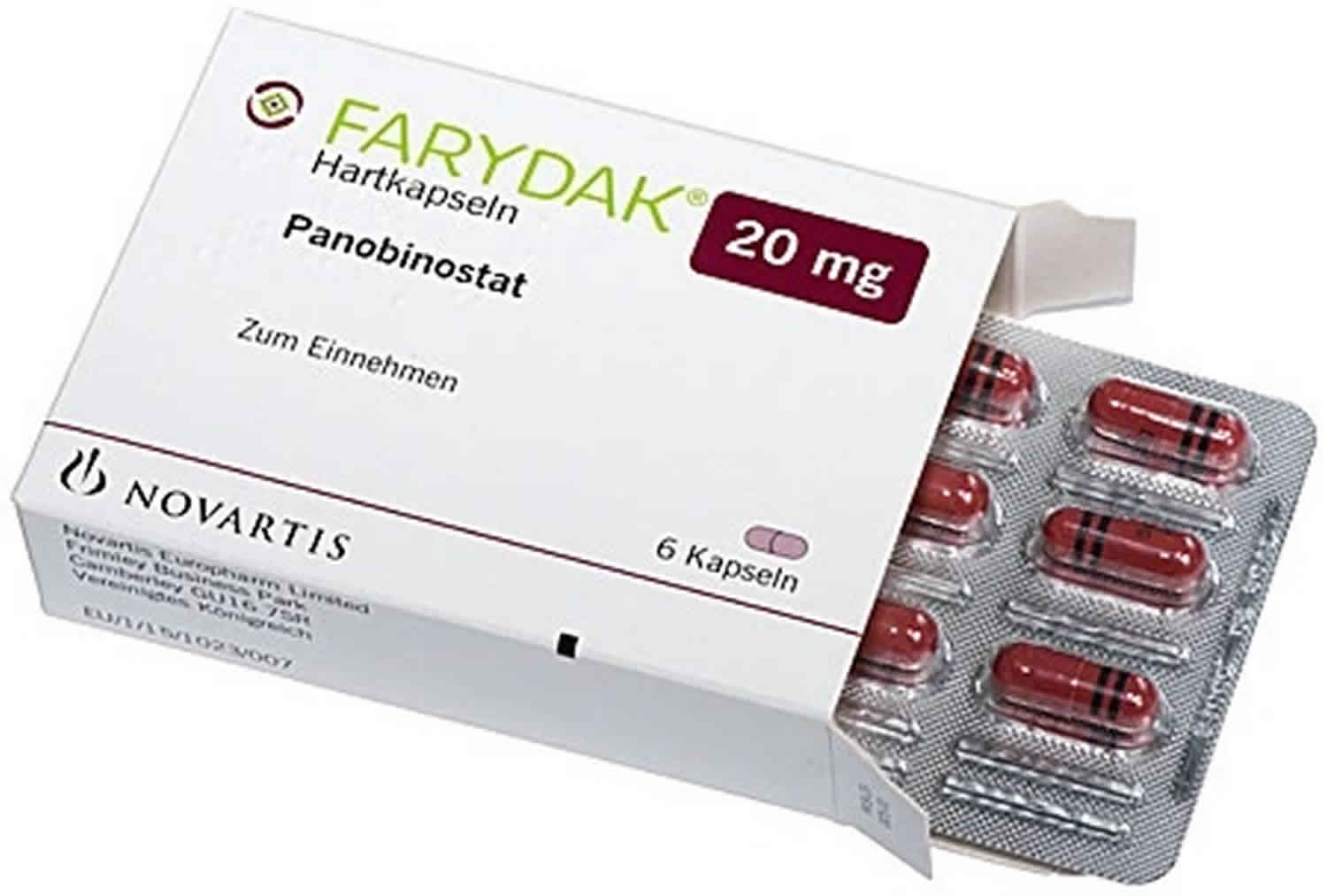
Panobinostat comes as a capsule of 10, 15 or 20 mg under the brand name Farydak to be taken by mouth. It is usually taken with or without food once daily on certain days of a 21-day cycle. The cycle may be repeated for up to 16 cycles. Take panobinostat at around the same time on each scheduled day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take panobinostat exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Swallow the capsules whole with a glass of water; do not crush, chew, or open them. Handle the capsules as little as possible. If you touch a broken panobinostat capsule or the medicine in the capsule, wash that area of your body with soap and water. If the medicine in the capsule gets into your mouth, nose, or eyes, wash it away with plenty of water.
The recommended dose regimen is 20 mg three times weekly for two weeks in three week cycles until there is disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. If you vomit after taking panobinostat, do not take another dose. Continue your regular dosing schedule.
Side effects are common and may require dose modification. The most common adverse events of panobinostat are thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, anemia, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, fever, peripheral edema, cough and pruritus. Panobinostat therapy has also been associated with hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, hyponatremia and mild increases in serum creatinine. Uncommon, but serious adverse events include severe diarrhea and cardiovascular events such as cardiac ischemia, arrhythmias and EKG changes.
Be sure to tell your doctor how you are feeling during your treatment. Your doctor may decrease your dose of panobinostat or stop your treatment for a while or permanently, if you experience side effects of the medication.
Panobinostat may cause severe diarrhea and other serious gastrointestinal (affecting the stomach or intestines) side effects. Severe diarrhea occurred in 25% of Panobinostat treated patients. If you experience any of the following symptoms, call your doctor immediately: stomach cramps; loose stools; diarrhea; vomiting; or dry mouth, dark urine, decreased sweating, dry skin, and other signs of dehydration. Talk to your doctor about what you should do if you develop diarrhea during your treatment with Panobinostat. Also talk to your doctor before taking any laxatives or stool softeners while you are taking this medication.
Panobinostat may cause serious or life-threatening heart problems during your treatment. Tell your doctor if you have recently had a heart attack or if you have long QT syndrome (condition that increases the risk of developing an irregular heartbeat that may cause fainting or sudden death), angina (chest pain), or other heart problems. Your doctor will order tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG; test that records the electrical activity of the heart) before and during your treatment to see if it is safe for you to take panobinostat. If you experience any of the following symptoms, call your doctor immediately: chest pain, rapid, pounding, or irregular heart beat, lightheadedness, feeling faint, dizziness, blue-colored lips, shortness of breath, or swelling of the hands, arms, feet, ankles, or lower legs.
Keep all appointments with your doctor and the laboratory. Your doctor will order certain tests to check your body’s response to panobinostat.
Your doctor or pharmacist will give you the manufacturer’s patient information sheet (Medication Guide) when you begin treatment with panobinostat and each time you refill your prescription. Read the information carefully and ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions. You can also visit the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) website (https://www.fda.gov/media/91262/download) or the manufacturer’s website to obtain the Medication Guide.
Talk to your doctor about the risks of taking panobinostat.
Panobinostat multiple myeloma
Panobinostat is FDA approved to be used with bortezomib (Velcade) and dexamethasone to treat people with multiple myeloma. Panobinostat is used in patients who have already received at least two other standard medications, including bortezomib and an immunomodulating agent.
This use is approved under FDA’s Accelerated Approval Program. As a condition of approval, a confirmatory trial(s) must show that panobinostat provides a clinical benefit in these patients.
Panobinostat is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer.
Panobinostat special precautions
Before taking panobinostat:
- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to panobinostat, any other medications, or any of the ingredients in panobinostat capsules. Ask your pharmacist or check the Medication Guide for a list of the ingredients.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what other prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you are taking or plan to take. Be sure to mention any of the following: amiodarone (Cordarone, Nexterone, Pacerone); antifungals such as itraconazole (Onmel, Sporanox), ketoconazole (Nizoral), posaconazole (Noxafil), and voriconazole (Vfend); atomoxetine (Strattera); bepridil (Vascor; no longer available in the U.S.); boceprevir (Victrelis); carbamazepine (Carbatrol, Tegretol, Teril, others); chloroquine (Aralen); clarithromycin (Biaxin, in PrevPac); conivaptan (Vaprisol); desipramine (Norpramin); dextromethorphan; disopyramide (Norpace); dolasetron (Anzemet); certain medications for HIV such as indinavir (Crixivan), lopinavir/ritonavir (Kaletra), nelfinavir (Viracept), ritonavir (Norvir, in Kaletra, in Viekira Pak), saquinavir (Invirase); methadone (Dolophine, Methadose); metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol-XL); moxifloxacin (Avelox); nebivolol (Bystolic); nefazodone; ondansetron (Zofran, Zuplenz); perphenazine; pimozide (Orap); phenobarbital; phenytoin (Dilantin, Phenytek); procainamide; quinidine (in Nuedexta); rifampin (Rifadin, Rimactane, in Rifamate, in Rifater); sotalol (Betapace, Sorine, Sotylize); telaprevir (Incivek; no longer available in U.S.); telithromycin (Ketek); thioridazine; tolterodine (Detrol); and venlafaxine (Effexor). Your doctor may need to change the doses of your medications or monitor you carefully for side effects.
- tell your doctor what herbal products you are taking, especially St John’s wort.
- tell your doctor if you have an infection or have or have ever had bleeding problems or liver disease.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Panobinostat may harm the fetus. Use birth control to prevent pregnancy during your treatment with panobinostat and for at least 1 month after the last dose. If you are a man and your partner can become pregnant, you should use a condom while taking this medication and for 90 days after your treatment is completed. Ask your doctor if you have questions about types of birth control that will work for you. If you become pregnant while taking panobinostat, call your doctor immediately.
- tell your doctor if you are breastfeeding. You should not breastfeed while taking panobinostat.
- if you are having surgery, including dental surgery, tell the doctor or dentist that you are taking panobinostat.
What special dietary instructions should I follow?
Do not eat pomegranate, grapefruit or star fruit or drink grapefruit or pomegranate juice while taking this medication.
Panobinostat dosage
Follow all directions on your prescription label. Do not take panobinostat in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended.
Panobinostat is usually given in combination with other medicines (bortezomib [Velcade] and dexamethasone). Follow your doctor’s dosing instructions very carefully.
The recommended starting dose of Panobinostat is 20 mg, taken orally once every other day for 3 doses per week in Weeks 1 and 2 of each 21-day cycle for up to 8 cycles. Consider continuing treatment for an additional 8 cycles for patients with clinical benefit who do not experience unresolved severe or medically significant toxicity. The total duration of treatment may be up to 16 cycles (48 weeks). Panobinostat is administered in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone as shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
The recommended dose of bortezomib is 1.3 mg/m2 given as an injection. The recommended dose of dexamethasone is 20 mg taken orally per scheduled day, on a full stomach.
Panobinostat is given in a 21- day treatment cycle, and you may only need to take the medicine during the first 1 to 2 weeks of each cycle. Your doctor will determine how long to treat you with panobinostat.
You may take panobinostat with or without food. Try to take the medicine at the same time on each scheduled day.
Take panobinostat with a full glass of water.
Do not open, crush or chew a panobinostat capsule. Swallow it whole. Do not use a broken capsule. The medicine from a broken capsule can be dangerous if it gets in your eyes, mouth, or nose, or on your skin. If this occurs, wash your skin with soap and water or rinse your eyes with water. Ask your doctor or pharmacist how to safely handle and dispose of a broken capsule.
If you vomit after taking panobinostat, do not take another capsule. Take your next dose as scheduled.
Panobinostat can cause severe diarrhea. You may be given medicine to prevent diarrhea or other side effects while you are receiving panobinostat.
Panobinostat can lower blood cells that help your body fight infections and help your blood to clot. Your blood will need to be tested often. Your heart function may need to be checked using an electrocardiograph or ECG (sometimes called an EKG). Your cancer treatments may be delayed based on the results of these tests.
Store the capsules in their original container at room temperature away from moisture, heat, and light.
Table 1: Recommended dosing schedule of Panobinostat in combination with Bortezomib and Dexamethasone during Cycles 1 to 8
| 21-Day Cycle | |||||||||||||||
| Cycles 1 to 8 (3-Week cycles) | Week 1 Days | Week 2 Days | Week 3 | ||||||||||||
| Panobinostat | 1 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 12 | Rest period | ||||||||
| Bortezomib | 1 | 4 | 8 | 11 | Rest period | ||||||||||
| Dexamethasone | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 11 | 12 | Rest period | ||||||
Table 2: Recommended dosing schedule of Panobinostat in combination with Bortezomib and Dexamethasone during Cycles 9 to 16
| 21-Day Cycle | |||||||||||||||
| Cycles 9 to 16 (3-Week cycles) | Week 1 Days | Week 2 Days | Week 3 | ||||||||||||
| Panobinostat | 1 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 12 | Rest period | ||||||||
| Bortezomib | 1 | 8 | Rest period | ||||||||||||
| Dexamethasone | 1 | 2 | 8 | 9 | Rest period | ||||||||||
What happens if I miss a dose?
If you are less than 12 hours late in taking your medicine, take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to make up the missed dose.
Panobinostat administration and monitoring instructions
Panobinostat should be taken orally once on each scheduled day at about the same time, either with or without food.
Panobinostat capsules should be swallowed whole with a cup of water. Do not open, crush, or chew the capsules.
If a dose is missed it can be taken up to 12 hours after the specified dose time. If vomiting occurs the patient should not repeat the dose, but should take the next usual scheduled dose.
Counsel patients on the correct dosing schedule, technique of administration of Panobinostat, and when to take Panobinostat if dosing adjustments are made.
Prior to the start of Panobinostat treatment and during treatment, monitoring should include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Obtain a CBC before initiating treatment. Verify that the baseline platelet count is at least 100 x 109/L and the baseline absolute neutrophil count (ANC) is at least 1.5 x 109/L. Monitor the CBC weekly (or more often as clinically indicated) during treatment.
- ECG: Perform an ECG prior to the start of therapy and repeat periodically during treatment as clinically indicated. Verify that the QTcF is less than 450 msec prior to initiation of treatment with Panobinostat. If during treatment with Panobinostat, the QTcF increases to ≥480 msec, interrupt treatment. Correct any electrolyte abnormalities. If QT prolongation does not resolve, permanently discontinue treatment with Panobinostat. During the clinical trial, ECGs were performed at baseline and prior to initiation of each cycle for the first 8 cycles.
- Serum Electrolytes: Obtain electrolytes, including potassium and magnesium, at baseline and monitor during therapy. Correct abnormal electrolyte values before treatment. During the trial, monitoring was conducted prior to the start of each cycle, at Day 11 of cycles 1 to 8, and at the start of each cycle for cycles 9 to 16.
For additional information please refer to the bortezomib and dexamethasone prescribing information.
Panobinostat Dose Adjustments
Dose modifications for use in Hepatic Impairment
Reduce the starting dose of Panobinostat to 15 mg in patients with mild hepatic impairment and 10 mg in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. Avoid use in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Monitor patients frequently for adverse events and adjust dose as needed for toxicity.
Dose modifications for use with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Reduce the starting dose of Panobinostat to 10 mg when coadministered with strong CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., boceprevir, clarithromycin, conivaptan, indinavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole, lopinavir/ritonavir).
Adverse drug reaction management:
- Reduce dose by 5 mg increments.
- If dosing reduced below 10 mg given 3 times per week, discontinue drug.
- Keep the same treatment schedule (3-week cycle) during dose reduction.
Anemia:
- Hemoglobin (Hb) less than 8 g/dL, Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Grade 3:
- Interrupt treatment until Hb 10 g/dL or greater; restart at reduced dose.
- CONCOMITANT USE WITH STRONG CYP450 3A INHIBITORS:
- Reduce starting dose to 10 mg orally.
Diarrhea:
- Moderate diarrhea (4 to 6 stools/day), CTCAE Grade 2: Interrupt treatment until resolved; restart at same dose.
- Severe diarrhea (7 stools or more/day), IV fluids or hospitalization required, CTCAE Grade 3: Interrupt treatment until resolved; restart at reduced dose.
- Life-threatening diarrhea, CTCAE Grade 4: Permanently discontinue drug.
Nausea or vomiting:
- Severe nausea, CTCAE Grade 3/4: Interrupt treatment until resolved then restart at reduced dose.
- Severe/Life-threatening vomiting, CTCAE Grade 3/4: Interrupt treatment until resolved then restart at reduced dose.
Neutropenia:
- Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) 0.75 to 1.0 x 109/L, CTCAE Grade 3: Maintain dose.
- ANC 0.5 to 0.75 x 10(9)/L, CTCAE Grade 3 (2 or more occurrences): Interrupt dose until ANC 1.0 x 10(9)/L or greater then restart at same dose.
- ANC less than 1.0 x 10(9)/L, CTCAE Grade 3 with febrile neutropenia (any grade): Interrupt dose until febrile neutropenia resolves and ANC 1.0 x 10(9)/L or greater then restart at reduced dose.
- ANC less than 0.5 x 10(9)/L, CTCAE Grade 4: Interrupt dose until ANC 1.0 x 10(9)/L or greater then restart at reduced dose.
Other grade 3/4 adverse reactions:
- Grade 3/4 adverse drug reactions other than thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, or gastrointestinal toxicity:
- Common Toxicity Criteria (CTC) Grade 2 toxicity recurrence and CTC Grade 3/4: Omit the dose until recovery to CTC Grade 1 or less and restart treatment at a reduced dose.
- CTC Grade 3/4 toxicity recurrence: Consider a further dose reduction once the adverse events have resolved to CTC Grade 1 or less.
Thrombocytopenia:
- Platelets less than 50 x 10(9)/L, CTCAE Grade 3: Maintain dose; monitor platelet counts at least weekly.
- Platelets less than 50 x 10(9)/L with bleeding, CTCAE Grade 3: Interrupt treatment; monitor platelet counts at least weekly until 50 x 10(9)/L or greater then restart at reduced dose.
- Platelets less than 25 x 10(9)/L, CTCAE Grade 4: Interrupt treatment; monitor platelet counts at least weekly until 50 x 10(9)/L or greater then restart at reduced dose.
Panobinostat side effects
Panobinostat can cause serious side effects, including:
- Diarrhea is common with Panobinostat and can be severe. See your healthcare provider right away if you have abdominal (stomach) cramps, loose stool, diarrhea, or if you feel like you are becoming dehydrated. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medicines to help prevent or treat these side effects. Taking or using stool softeners or laxative medicines may worsen diarrhea, talk to your healthcare provider before taking or using these medicines. Your healthcare provider will do regular tests to check the levels of fluid and electrolytes in your blood during treatment with panobinostat.
- Heart problems. Panobinostat can cause severe heart problems which can lead to death. Your risk of heart problems may be increased if you have a condition called “long QT syndrome” or other heart problems. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your electrolytes and do an electrocardiogram (ECG) tests before and during treatment with panobinostat. See your healthcare provider and get emergency medical help right away if you have any of the following symptoms of heart problems:
- chest pain
- dizziness
- faster or slower heart beat
- blue colored lips
- palpitations (feel like your heart is racing)
- shortness of breath
- feel lightheaded or faint
- swelling in your leg
- Bleeding. Panobinostat can cause severe bleeding which can lead to death. It may take you longer than usual to stop bleeding while you are taking panobinostat. Your healthcare provider will check your platelet counts before you start panobinostat and during your treatment with panobinostat. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following signs of bleeding:
- blood in your stools or black stools (look like tar)
- increased bruising
- pink or brown urine
- feeling dizzy or weak
- unexpected bleeding or bleeding that is severe or that you cannot control
- confusion
- vomit blood or vomit looks like coffee grounds
- change in your speech
- cough up blood or blood clots
- headache that lasts a long time
Panobinostat may cause other side effects. See your doctor if you have any unusual problems while taking panobinostat.
What happens if I overdose?
Symptoms of Panobinostat overdose may include the following:
- diarrhea
- nausea
- vomiting
- decreased appetite
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222. Information is also available online at https://www.poisonhelp.org/help
References