Acoustic trauma
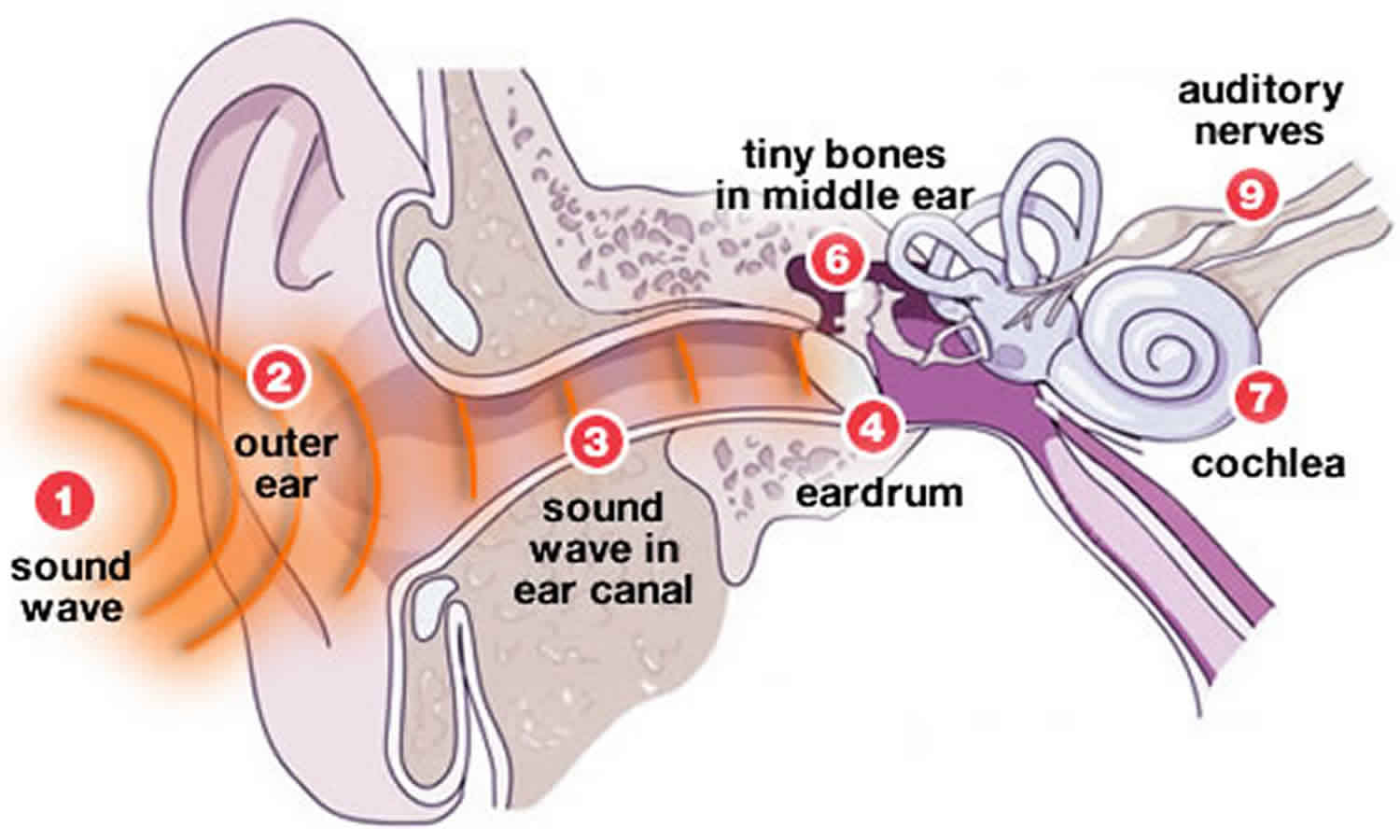
Acoustic trauma is injury to the hearing mechanisms in the inner ear that is often caused by exposure to very loud noise (100-150 dB) 1. Acoustic trauma is a common cause of sensory hearing loss. Acoustic trauma can occur after exposure to a single very loud noise or from exposure to noises at significant decibels over a longer period of time.
Acoustic trauma can be caused by a sudden and powerful sound like an explosion. Explosions often lead to damaged ear drums and consequently conductive hearing loss.
Many people have experienced a period of reduced hearing after exposure to loud sounds, for example after a concert or a visit to a discotheque or after having worked with noisy equipment. This kind of hearing impairment is often temporary. After some time acoustic trauma will stop.
If the acoustic trauma continues, it will typically lead to hearing impairment within a relatively narrow frequency around 4 kHz. In other words, the person with an acoustic trauma will be unable to hear within a certain range of high frequency tones.
In certain daily situations, this may not bother people. But in more noisy environments, people with an acoustic trauma may have problems hearing. Sometimes a hearing aid can be of help to people suffering from permanent acoustic trauma.
Acoustic trauma causes
Damage to the hearing mechanisms within the inner ear may be caused by:
- Explosion near the ear
- Firing a gun near the ear
- Long-term exposure to loud noises such as loud music or machinery.
In a military environment, acoustic trauma is caused by noise from weapons and equipment systems, turbine engines, and high-performance aircraft and helicopters 2. Speech discrimination can be affected and cases of total unilateral deafness have been reported 3. The noise, as reported by the patient, is usually unexpected, intense, and of short duration 4.
Acoustic trauma symptoms
Acoustic trauma symptoms include:
- Partial hearing loss that most often involves exposure to high-pitched sounds. The hearing loss may slowly get worse.
- Noises, ringing in the ear (tinnitus).
Acoustic trauma complications
Progressive hearing loss is the main complication of acoustic trauma.
Tinnitus (ear ringing) can also occur.
Acoustic trauma diagnosis
Your doctor will most often suspect acoustic trauma if hearing loss occurs after noise exposure. A physical exam will determine if the eardrum is damaged. Audiometry may determine how much hearing has been lost.
Acoustic trauma treatment
Acoustic trauma hearing loss may not be treatable. The goal of treatment is to protect the ear from further damage. Eardrum repair may be needed.
A hearing aid may help you communicate. You can also learn coping skills, such as lip reading.
Acoustic trauma prognosis
Acoustic trauma hearing loss may be permanent in the affected ear. Wearing ear protection when around sources of loud sounds may prevent the hearing loss from getting worse.
- Choi C-H, Du X, Floyd RA, Kopke RD. Therapeutic effects of orally administrated antioxidant drugs on acute noise-induced hearing loss. Free Radical Research. 2014;48(3): 264-72.[↩]
- Xiong M, Lai H, Yang C, Huang W, Wang J, Fu X et al. Comparison of the Protective Effects of Radix Astragali, a-Lipoic Acid, and Vitamin E on Acute Acoustic Trauma. Ear, Nose and Throat. 2012;5:25-31.[↩]
- Moon IS, Park SY, Park HJ, Yang HS, Hong SJ, Lee WS. Clinical Characteristics of Acoustic Trauma Caused by Gunshot Noise in Mass Rifle Drills without Ear Protection. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene. 2011;8:618-23.[↩]
- Mora-Magaiia I, Collado-Coronab MA, Toral-Martifibn R, Cano A. Acoustic trauma caused by lightning. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1996;35:59-68. 13/ Lonsbury-Martin, B.L. and Martin, G.K. (1986) In: Cummings, C.W. (Ed), Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. C.V. Mosby Company, St. Louis, MO, Chapter 170[↩]