What is Organic Foods
In order to find out if organic foods are better to eat, we must first find and compare the ‘opposite’ of organic foods, that is the non-organic foods. That way we can use ‘relativity’ to compare organic foods versus non-organic foods.
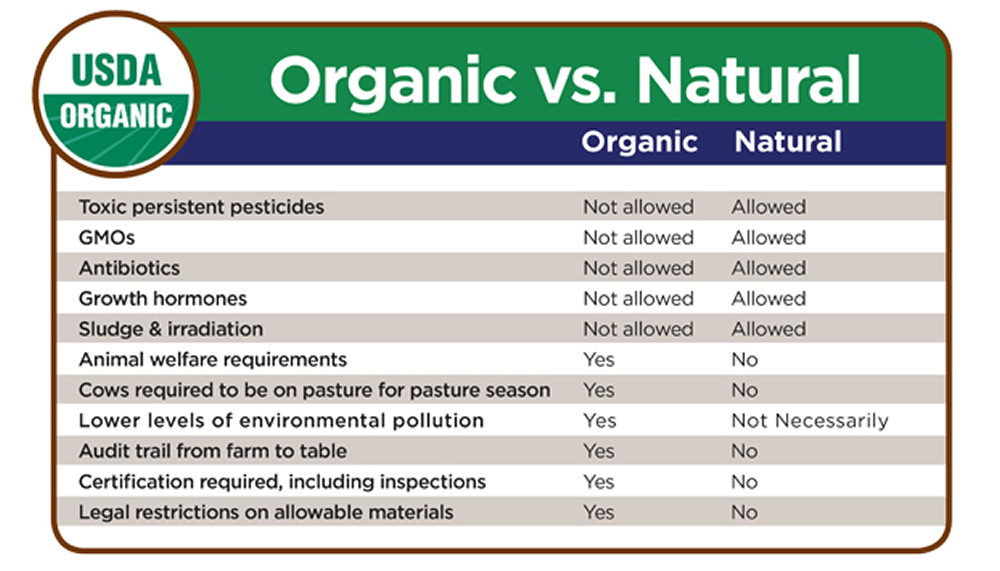
Put simply, if you see the “USDA Organic” or “Certified Organic” seal on your food, the item must have an ingredients list and the contents should be 95% or more certified organic, meaning free of synthetic additives like pesticides, chemical fertilizers, and dyes, and must not be processed using industrial solvents.
Simply stated, organic produce and other ingredients are grown without the use of pesticides, synthetic fertilizers, sewage sludge, genetically modified organisms, or ionizing radiation. Animals that produce meat, poultry, eggs, and dairy products do not take antibiotics or growth hormones.
Before a product can be labeled “organic,” a Government-approved certifier inspects the farm where the food is grown to make sure the farmer is following all the rules necessary to meet USDA organic standards. Companies that handle or process organic food before it gets to your local supermarket or restaurant must be certified, too.
How different is organic foods as compared to food from non-organic foods ?
The USDA has identified for three categories of labeling organic products:
1) 100% Organic: Made with 100% organic ingredients
2) Organic: Made with at least 95% organic ingredients
3) Made With Organic Ingredients: Made with a minimum of 70% organic ingredients with strict restrictions on the remaining 30% including no GMOs (genetically modified organisms)
Products with less than 70% organic ingredients may list organically produced ingredients on the side panel of the package, but may not make any organic claims on the front of the package.
The organic foods rationale
People who buy organic usually cite these reasons for their decision:
- They’re safer. Fruits and vegetables labeled as organic are generally grown without chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Livestock raised under organic practices aren’t fed antibiotics or growth hormones.
- They’re kinder to the environment. Organic farming practices are designed to be more sustainable, emphasizing conservation and reducing pollutants.
- They’re healthier. A few studies have suggested organic foods might be higher in nutrients than their traditional counterparts.
Of these three reasons, the health claims for organic foods have been the most tenuous. To investigate these claims, researchers at Stanford University evaluated nearly 250 studies comparing the nutrients in organic vs. natural foods (fruits, vegetables, grains, poultry, meat, and eggs), and the health outcomes of eating these foods.
The researchers discovered very little difference in nutritional content, aside from slightly higher phosphorous levels in many organic foods, and a higher omega-3 fatty acid content in organic milk and chicken.
So is organic food more nutritious than conventional food ?
At this time, there is no definitive research that makes this claim.
However, some recently published studies in peer-reviewed journals have shown organic foods to have higher nutritional value. For example, researchers at the University of California, Davis, recently found that organic tomatoes had higher levels of phytochemicals and vitamin C than conventional tomatoes.
Organic produce did have the slight edge in food safety, with 30% lower pesticide residues than conventional foods. In general, pesticide levels in both organic and non-organic foods were within allowable safety limits. It’s still not clear, though, just what that means to consumers’ health. Just because these foods aren’t going over what they call an ‘acceptable limit’ doesn’t mean they’re safe for everyone. There haven’t been enough studies evaluating pesticide exposure to confirm the health effects, particularly in children and pregnant women.
Organic chicken and pork were also about a third less likely to contain antibiotic-resistant bacteria than conventionally raised chicken and pork. However, the bacteria that cause food poisoning were equally present in both types of foods.
Should you buy and eat organic foods ?
That’s a decision only you can make based on your family’s needs and wants and your budget. If you’re buying organic solely for better nutrition, based on this review there’s no evidence you’re gaining any real advantages. But if you’re concerned about pesticides and you can afford organics, it might be worth it to buy them.
For many people, cost is the deciding factor. Organic foods are more expensive and often significantly more so than non-organic foods. A visit to your local supermarket should reveal the huge price difference between non-organic and organic foods.