Chadwick sign
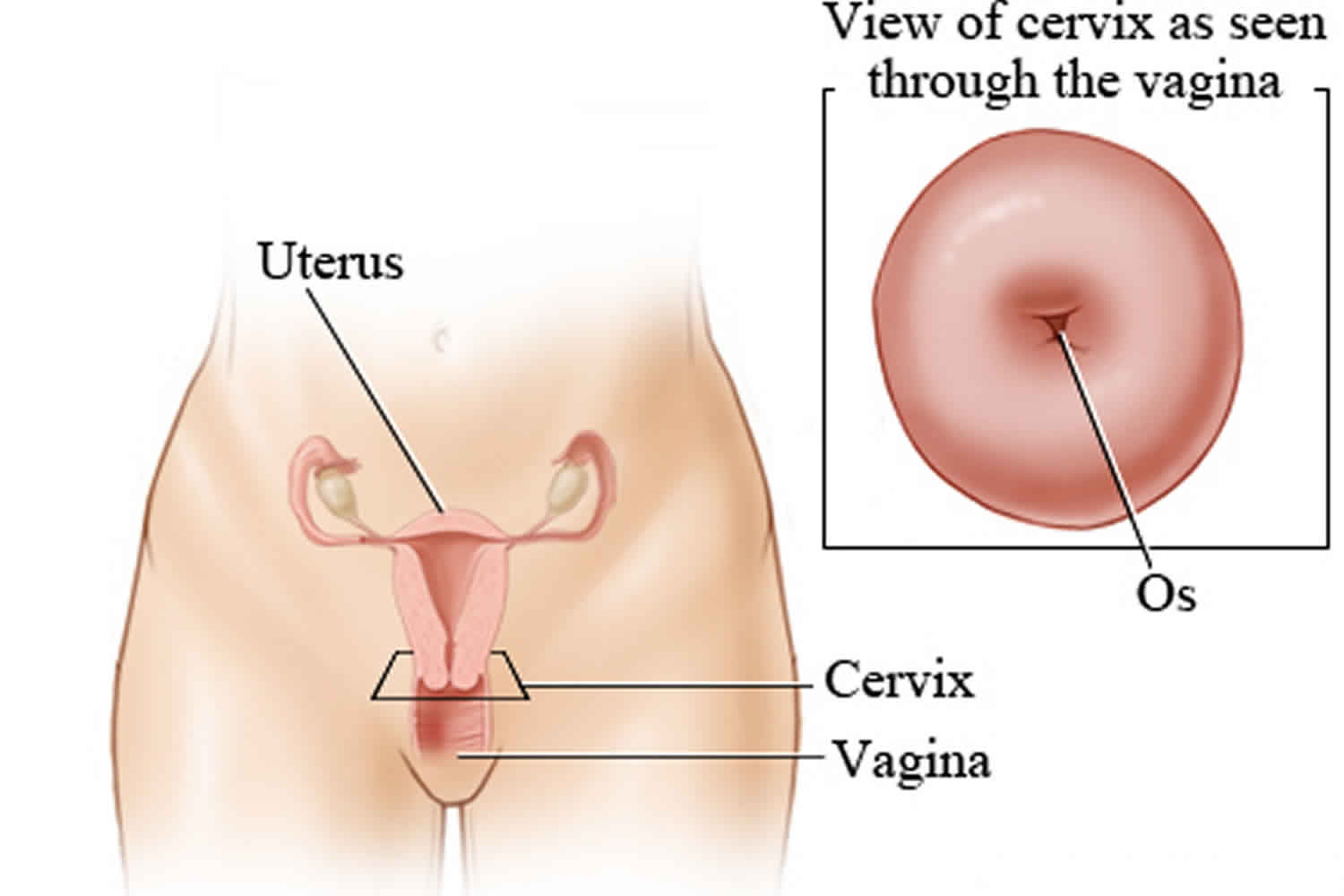
Chadwick sign is a bluish discoloration of the cervix, vagina and vulva caused by venous congestion. Chadwick’s sign can be observed as early as 6-8 weeks after conception, and is often used as an early sign of pregnancy.
The diagnosis of pregnancy requires a multifaceted approach using 3 main diagnostic tools. These are history and physical examination, laboratory evaluation, and ultrasonography. Currently, physicians may use all of these tools to diagnose pregnancy at early gestation and to help rule out other pathologies.
Important aspects of the menstrual history must be obtained. The woman should describe her usual menstrual pattern, including date of onset of last menses, duration, flow, and frequency. Items that may confuse the diagnosis of early pregnancy are an atypical last menstrual period, contraceptive use, and a history of irregular menses. Additionally, as many as 25% of women bleed during their first trimester, further complicating the assessment 1.
The classic presentation of pregnancy is a woman with menses of regular frequency who presents with absence of menstruation (amenorrhea), nausea, vomiting, generalized malaise, and breast tenderness.
Upon physical examination, one may find an enlarged uterus after bimanual examination, breast changes, and softening and enlargement of the cervix (Hegar sign; observed at approximately 6 weeks). A gravid uterus may be palpable low in the abdomen if the pregnancy has progressed far enough, usually by 12 weeks. Currently, through the use of chemical assays and ultrasonography, physicians are capable of making the diagnosis of pregnancy before many of the physical signs and symptoms are evident 2.
Several hormones can be measured and monitored to aid in the diagnosis of pregnancy. The most commonly used assays are for the beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (beta hCG). Other hormones that have been used include progesterone and early pregnancy factor.
Goodell’s sign
Goodell’s sign is an indication of pregnancy. It is a significant softening of the vaginal portion of the cervix.
Hegar’s sign
Hegar’s sign is an indication of pregnancy in a woman, specifically the compressibility and softening of the cervical isthmus (the portion of the cervix between the uterus and the vaginal portion of the cervix) and the uterine cervix appearing bluish and engorged.
The sign is usually present during second and third months of pregnancy from the fourth to sixth week. It is not a positive indicator of pregnancy, and its absence does not exclude pregnancy.
The indicator was originally described by Ernst Ludwig Alfred Hegar, a German gynecologist, in 1895. Hegar credits one of his students for discovering the sign.
- Paspulati RM, Bhatt S, Nour SG. Sonographic evaluation of first-trimester bleeding. Radiol Clin North Am. 2004 Mar. 42(2):297-314.[↩]
- Paul M, Schaff E, Nichols M. The roles of clinical assessment, human chorionic gonadotropin assays, and ultrasonography in medical abortion practice. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000 Aug. 183(2 Suppl):S34-43.[↩]