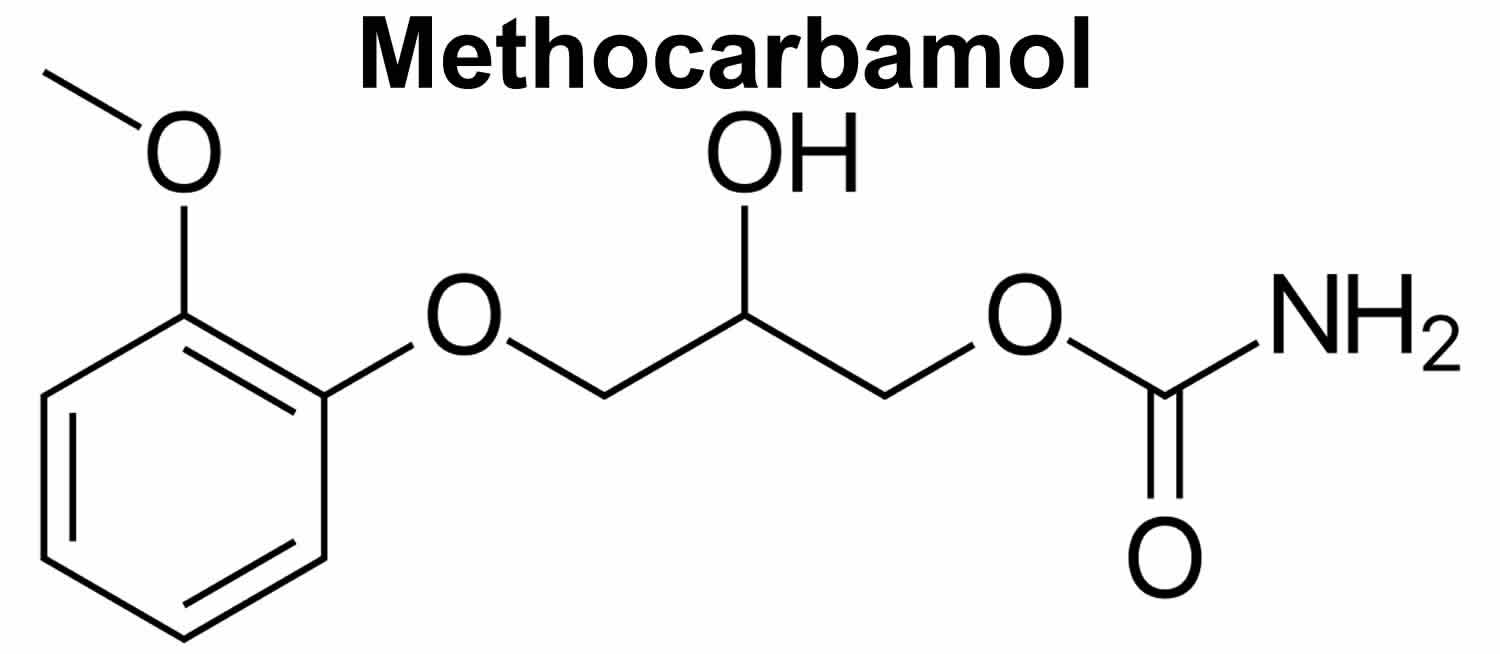
What is methocarbamol
Methocarbamol is a carbamate derivative of guaifenesin with centrally acting muscle relaxant properties whose mode of action has not been established. The mode of action of methocarbamol has not been clearly identified, but may be related to its sedative properties. Methocarbamol is in a class of medications called muscle relaxants. Methocarbamol is used as an adjunct in the symptomatic treatment of musculoskeletal conditions associated with painful muscle spasm. Though the exact mechanism of action of methocarbamol was not established, it’s postulated to be via a mechanism similar of carbamate, inhibition of acetylcholinesterase at synapses in the autonomic nervous system, neuromuscular junction, and central nervous system. Methocarbamol has no direct effect on the contractile mechanism of striated muscle, the motor end plate or the nerve fiber.
Methocarbamol is used with rest, physical therapy, and other measures to relax muscles and relieve pain and discomfort caused by strains, sprains, and other muscle injuries. Methocarbamol works by slowing activity in the nervous system to allow the body to relax.
Methocarbamol and alcohol
Additive CNS (central nervous system) depression may occur when methocarbamol is administered concomitantly with other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including alcohol 1. If methocarbamol is used concomitantly with other depressant drugs, caution should be used to avoid overdosage.
How should methocarbamol be used?
Methocarbamol comes as a tablet to take by mouth. It usually is taken four times a day at first, then it may be changed to three to six times a day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take methocarbamol exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Methocarbamol special precautions
Before taking methocarbamol:
- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to methocarbamol, any other medications or any of the ingredients in methocarbamol tablets. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of the ingredients.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you are taking or plan to take. Be sure to mention any of the following: medications for seizures, depression, colds, or coughs; sedatives; and tranquilizers.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking methocarbamol, call your doctor.
- talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of taking methocarbamol if you are 65 years of age or older. Older adults should not usually take methocarbamol because it is not as safe or as effective as other medications that can be used to treat the same condition.
- you should know that this medication may make you drowsy. Do not drive a car or operate machinery until you know how methocarbamol affects you.
- talk to your doctor about the safe use of alcohol during your treatment with this medication. Alcohol can make the side effects of methocarbamol worse.
- Additive CNS (central nervous system) depression may occur when methocarbamol is administered concomitantly with other CNS depressants, including alcohol 1. If methocarbamol is used concomitantly with other depressant drugs, caution should be used to avoid overdosage.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Pregnancy Category C: Animal reproduction studies have shown an adverse effect on the fetus and there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in humans, but potential benefits may warrant use of the drug in pregnant women despite potential risks.
Safe use of methocarbamol has not been established with regard to possible adverse effects upon fetal development. There have been reports of fetal and congenital abnormalities following in utero exposure to methocarbamol. Therefore, methocarbamol should not be used in women who are or may become pregnant and particularly during early pregnancy unless in the judgment of the physician the potential benefits outweigh the possible hazards.
Methocarbamol and breastfeeding
Methocarbamol and/or its metabolites are excreted in the milk of dogs; however, it is not known whether methocarbamol or its metabolites are excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when methocarbamol is administered to a nursing woman.
Methocarbamol uses
Methocarbamol is a muscle relaxant and is indicated as an adjunct to rest, physical therapy, and other measures for the relief of discomfort associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions. Methocarbamol works by blocking nerve impulses (or pain sensations) that are sent to your brain. Methocarbamol does not directly relax tense skeletal muscles in man.
Methocarbamol is used together with rest and physical therapy to treat skeletal muscle conditions such as pain or injury.
Methocarbamol medication may be prescribed for other uses. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
Methocarbamol dosage
Adult Dose for Muscle Spasm
Oral:
- Initial dose: 1500 mg four times a day for the first 48 to 72 hours, up to a maximum dosage of 8 g/day for severe symptoms.
- Maintenance dose: 4000 to 4500 mg/day in divided doses.
IV or IM:
The injectable preparation of methocarbamol is intended for IV or IM use only.
- 1000 mg up to every 8 hours if necessary, not to exceed 3 g/day for more than 3 consecutive days except in the treatment of tetanus. A like course may be repeated after a lapse of 48 hours if the condition persists. Oral therapy should be instituted as soon as possible. For symptoms of moderate severity, oral doses may be adequate after one injection if patient can tolerate oral medications.
Injectable methocarbamol may be administered undiluted directly into the vein at a maximum rate of 3 mL (300 mg) per minute. It may also be added to an intravenous infusion of Sodium Chloride Injection or 5% Dextrose Injection. One vial given as a single dose should not be diluted to more than 250 mL for IV infusion. Care should be exercised to avoid vascular extravasation of the solution, which may result in thrombophlebitis. Patient should preferably be in a recumbent position during and for at least 10 to 15 minutes following the injection.
When given intramuscularly, not more than 5 mL should be injected into each gluteal region.
Adult Dose for Tetanus
- 1 to 2 g directly into IV tubing, followed by an additional 1 to 2 g by IV infusion for a total dose of up to 3 g initially. This procedure may be repeated every 6 hours until nasogastric tube can be inserted. Then, crushed tablets suspended in water or saline solution can be given through the nasogastric tube. Total daily oral doses up to 24 g may be required.
Pediatric Dose for Tetanus
- Initial dose: 15 mg/kg/dose IV or 500 mg/m2/dose IV, may repeat every 6 hours if needed.
- Maximum dose: 1.8 g/m2/day IV for 3 days only
Renal Dose Adjustments
Use of the injectable form of methocarbamol is not recommended in patients with renal insufficiency due to the high concentration of polyethylene glycol in the solution.
Liver Dose Adjustments
Data not available
What should I do if I forget a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember it. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and continue your regular dosing schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one.
Methocarbamol side effects
Methocarbamol may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:
- drowsiness
- dizziness
- upset stomach
- blurred vision
- fever
- black, blue, or green discoloration of urine
If you experience either of the following symptoms, call your doctor immediately:
- rash
- itching
While the product label for methocarbamol states that it can cause jaundice (including cholestatic jaundice), there is little published evidence to suggest that methocarbamol is a cause of hepatic injury or clinically apparent drug induced liver disease. During clinical trials of methocarbamol, some patients had to stop treatment because of nausea, dizziness, or other nonspecific complaints, but no serum aminotransferase levels or other laboratory results were reported. Methocarbamol appears to be well tolerated, but the lack of monitoring of serum aminotransferase levels during clinical trials with methocarbamol makes it impossible to rule out the possibility of mild liver injury occurring with treatment.
Cardiovascular
- Cardiovascular side effects have included syncope, hypotension, and bradycardia.
Nervous system
- Nervous system side effects have included dizziness, lightheadedness, vertigo, headache, drowsiness, fainting, and mild muscular incoordination. Convulsions have been reported with intravenous administration, especially in patients with a history of epilepsy.
Dermatologic
- Dermatologic side effects have included urticaria, pruritus, rash, sloughing, thrombophlebitis, and pain at the injection site.
Ocular
- Ocular side effects have included blurred vision, conjunctivitis, nystagmus, and diplopia.
Respiratory
- Respiratory side effects have included nasal congestion, bronchospasm, and anaphylaxis.
Gastrointestinal
- Gastrointestinal side effects have included gastrointestinal upset, anorexia, and adynamic ileus.
Other
- Other side effects have included metallic taste and fever.
- Effects on lab tests have included a possible color interference in certain screening tests for 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) and vanillylmandelic acid (VMA).
Hematologic
- Hematologic side effects have included hemolysis, particularly with intravenous injection.
Renal
- Methocarbamol vials for injection contain polyethylene glycol 300 (PEG 300). Larger amounts of PEG 300 can increase preexisting renal acidosis and urea retention in patients with renal insufficiency.
- Renal side effects including urine discoloration (black, blue, brown, or green) have been reported after oral administration in some patients.
General
- General side effects have included angioneurotic edema.
Methocarbamol may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while you are taking this medication.
Methocarbamol overdose
Limited information is available on the acute toxicity of methocarbamol. Overdose of methocarbamol is frequently in conjunction with alcohol or other CNS depressants and includes the following symptoms: nausea, drowsiness, blurred vision, hypotension, seizures, and coma.
In post-marketing experience, deaths have been reported with an overdose of methocarbamol alone or in the presence of other CNS depressants, alcohol or psychotropic drugs.
Get emergency help immediately if any of the following symptoms of overdose occur while taking methocarbamol:
Symptoms of methocarbamol overdose:
- loss of consciousness
- shaking or jerking of one area or side of the body
Treatment of methocarbamol overdose
Management of overdose includes symptomatic and supportive treatment. Supportive measures include maintenance of an adequate airway, monitoring urinary output and vital signs, and administration of intravenous fluids if necessary. The usefulness of hemodialysis in managing overdose is unknown.