Myxoid cyst
A digital myxoid cyst also known as a digital mucous cyst, myxoid cyst, digital ganglion cyst, digital synovial cyst or pseudocyst, is a benign (harmless) growth usually occurring on the finger, usually occurs at the base of the nail on the fingers or toes. Digital myxoid cyst is called a pseudocyst because it is not surrounded by a capsule, unlike a true cyst. Digital myxoid cysts are not “catching” and they are not a sign of infection. Digital myxoid cysts are believed to form from deteriorated tissues. Myxoid cysts may be associated with osteoarthritis. Digital myxoid cysts do not develop into skin cancer.
Myxoid cysts are common and are more common in women and the elderly. These lesions occur more frequently on the fingers than on the toes.
Digital myxoid pseudocysts can be of two varieties. The first is a form of focal mucinosis, a condition characterized by abnormal deposits of mucopolysaccharides (mucins) in the skin. The other variation arises from extension of the lining of the finger joint and is due to osteoarthritis – a type of ganglion.
Myxoid cysts are benign, but patients may seek treatment if they become unsightly, cumbersome, or painful.
Some myxoid cysts will disappear spontaneously. Recurrence rates are high. Patients who fail conservative treatment may require referral to a dermatologic or hand surgeon. A number of treatment options are available. These include, most commonly:
- Repeated puncture
- Corticosteroid tape (flurandrenolide)
- Steroid injections (triamcinolone)
- Cryosurgery (freezing)
- Surgical excision
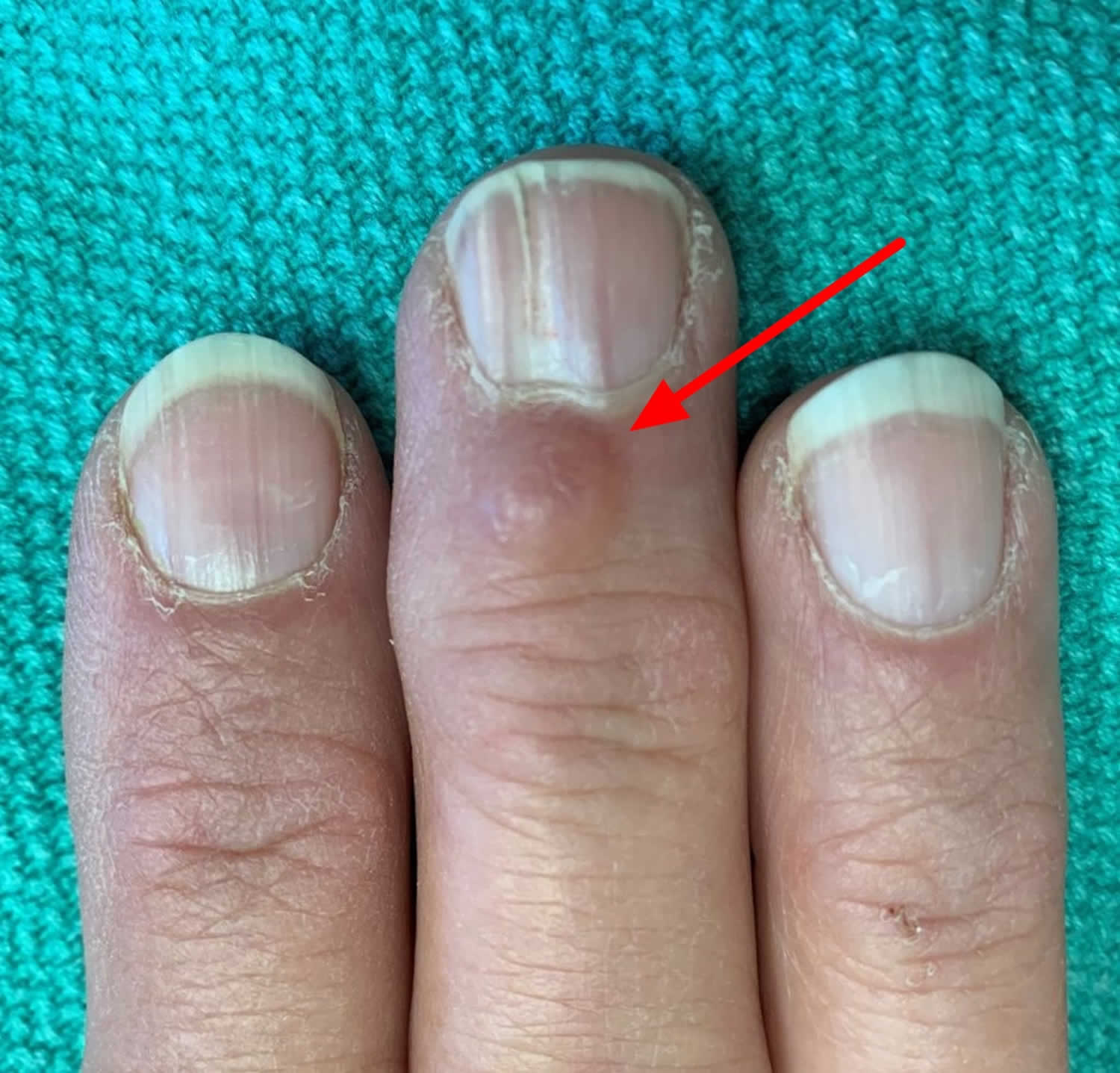
Figure 1. Digital myxoid cyst
Myxoid cyst causes
The exact cause of digital myxoid cyst is not known. Myxoid cyst is frequently connected to the lining of the finger or toenail joint and is usually located between the joint and the nail. Arthritis of the joint at the end of the finger or toe probably predisposes a person to developing these cysts. Digital myxoid cyst arises from degeneration in the connective tissue on the top of the last segment of the finger.
Myxoid cyst symptoms
The most common location for myxoid cysts is the fingers. Digital myxoid cyst is a solitary, rounded, skin-colored, reddish or slightly translucent bump or nodule that may feel relatively firm or may feel more fluid-filled (fluctuant). Digital myxoid cysts are usually found near the base of the nail, slightly off to one side or the other. If a cyst overlies the area where the nail is formed (beneath the nail or involve the root of the nail), it may cause changes in the nail, such as grooves or depressions along the length of the nail. Rarely, these cysts involve the fat pad of the fingertip. Sometimes, slightly sticky, clear, yellowish in color or blood-stained contents may leak out of the digital myxoid cyst. Most people usually develop only one cyst. However, some people may develop more than one cyst on different fingers.
Myxoid cyst is usually not painful. However, a cyst may become tender, especially when knocked. Occasionally, there may also be symptoms of arthritis with pain, stiffness and deformity of the joint.
Digital myxoid cysts may get in the way and their appearance may cause concern.
Digital myxoid cysts are tender when knocked but only rarely become infected. If a cyst suddenly becomes larger, painful, red and hot, you should see your doctor as these symptoms may indicate an infection and an antibiotic may be needed.
Myxoid cyst diagnosis
A digital myxoid cyst is usually easily recognized as a small lump overlying the end joint of a finger or toe. There may or may not be a groove present in the adjacent fingernail. If the skin over the top of the cyst is broken, a discharge of clear, slightly sticky material from the cyst is characteristic.
If the cyst arises under the nail the diagnosis is more difficult. The overlying nail is often deformed. If the diagnosis is not certain, your physician may recommend further testing, such as an X-ray, ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI. A biopsy (sample taken from the cyst with a local anesthetic) may be needed.
Myxoid cyst treatment
If a digital myxoid cyst does not cause any symptoms, no treatment is required. Small cysts can disappear spontaneously without treatment.
If treatment is considered necessary, there are a number of options.
Treatments which may be successful for digital myxoid pseudocyst include:
- Repeatedly pressing firmly on the cyst
- Squeezing out its contents (make a hole with a sterile needle)
- Cryotherapy (freezing)
- Steroid injection
- Sclerosant injection
- Surgical removal.
Unfortunately, digital myxoid pseudocysts often recur, whatever treatment is used.
Without local anesthetic
- Repeated drainage of the cyst fluid using a sterile needle or blade
With local anesthetic
- Excision of the digital mucous cyst
- Injecting dye into the joint to find the cyst and point of leakage from the joint. Then closing that leak.
- Cauterising the cyst
Myxoid cyst prognosis
Digital myxoid cysts may recur even after treatment. They may also disappear spontaneously.