Pili multigemini
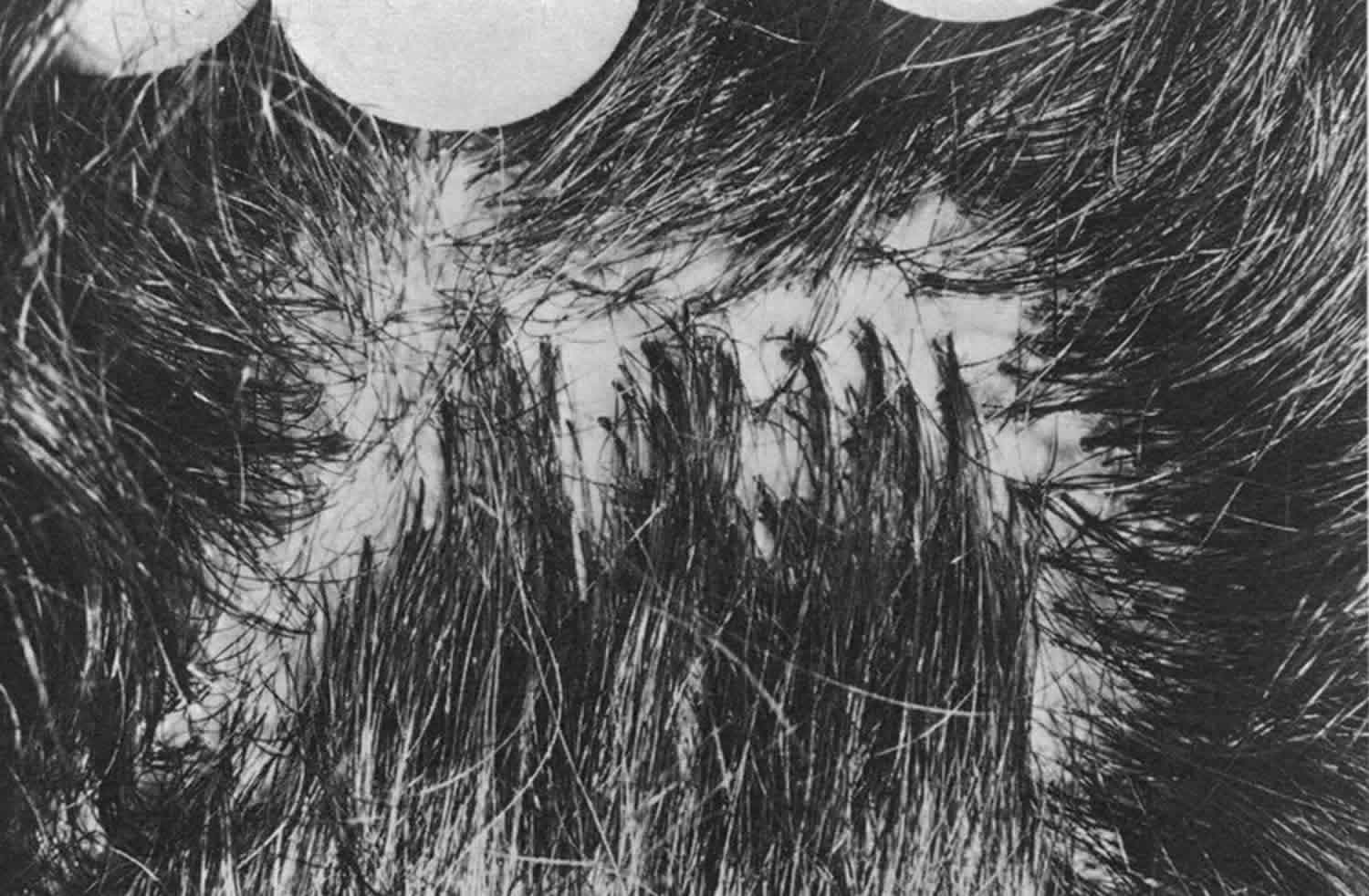
Pili multigemini also called tufted hair, is an unusual hair follicle dysplasia, characterized by multiple hair shafts bunched together that emerge from a single hair follicle like a toothbrush or doll’s hair 1. Normal hair grows from a single hair follicle and exits from one hair canal to the surface of the skin. In pili multigemini, light microscopy confirms that all the hairs are surrounded by a single outer root sheath. A common bulb encloses a dermal papilla that splits into different-sized hair shafts with separate cuticles 2. The hair shafts are normal. Pili multigemini is frequently seen on the beard of adult men and the scalp of children 3. Extensive pili multigemini involving large areas has rarely been described 4.
Tufted hair or pili multigemini is a feature of scarring inflammatory scalp conditions, particularly the severe forms of scalp folliculitis known as folliculitis decalvans and dissecting cellulitis.
Pili multigemini causes
The cause of pili multigemini is unknown, although there may be a genetic link. It has been suggested that a subdivided papilla produced divided hairs or that multiple hairs may be due to the partial merging of several papillae. Other possibility is the reactivation of silent embryonic epithelial germs result in multigeminate hairs 3.
Pili multigemini symptoms
Pili multigemini or tufted hair, is characterized by multiple hair shafts bunched together that emerge from a single hair follicle like a toothbrush or doll’s hair 1. Normal hair grows from a single hair follicle and exits from one hair canal to the surface of the skin. Pili multigemini is frequently seen on the beard of adult men and the scalp of children 3. Extensive pili multigemini involving large areas has rarely been described 4.
Pili multigemini diagnosis
Diagnosis of pili multigemini is visual 5. Dermoscopy of hair and scalp (trichoscopy) enhances the evaluation of hair disorders and facilitates the diagnosis of this rare hair shaft dysplasia 6.
Pili multigemini differential diagnosis
Pili multigemini differential diagnosis includes mainly pili bifurcate, which is characterized by bifurcation of the hair shaft. Two features define this dysplasia. Each bifurcation produces two separate parallel branches, which fuse again to form a single shaft, and each branch of the successive bifurcations is covered with its own cuticle 7. However, in pili gemini, a kinetic papilla splits at the upper end from single to double-tipped during the anagen phase and consequently the same follicular matrix produces two different-sized hair shafts having separate cuticles that emerge through a single pilary canal. Pili gemini maintains the double tipped papilla and consequently the hair shaft does not fuse again.
Pili multigemini treatment
At present, there is no specific treatment for pili multigemini.
- De Berker D, Sinclair R. Rook A, Dawber R. Diseases of the Hair and Scalp. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific; 1997. Defects of the hair shaft; pp. 239–98.[↩][↩]
- Lester L, Venditti C. The prevalence of pili multigemini. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:1362–3.[↩]
- Cambiaghi S, Barbareschi M, Cambiaghi G, Caputo R. Scanning electron microscopy in the diagnosis of pili multigemini. Acta Derm Venereol. 1995;75:170–1.[↩][↩][↩]
- Lee JS, Kim YC, Kang HY. The nevoid pili multigemini over the back. Eur J Dermatol. 2005;15:99–101.[↩][↩]
- Ciudad-Blanco C, Montero EC, Heffernan JA, Ochaita PL. Extensive pili multigemini over the back. Int J Trichology. 2014;6(4):180–181. doi:10.4103/0974-7753.142871 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4212297[↩]
- Rudnicka L, Rakowska A, Olszewska M. Trichoscopy: How it may help the clinician. Dermatol Clin. 2013;31:29–41.[↩]
- Camacho FM, Happle R, Tosti A, Whiting D. The different faces of pili bifurcati. A review. Eur J Dermatol. 2000;10:337–40.[↩]