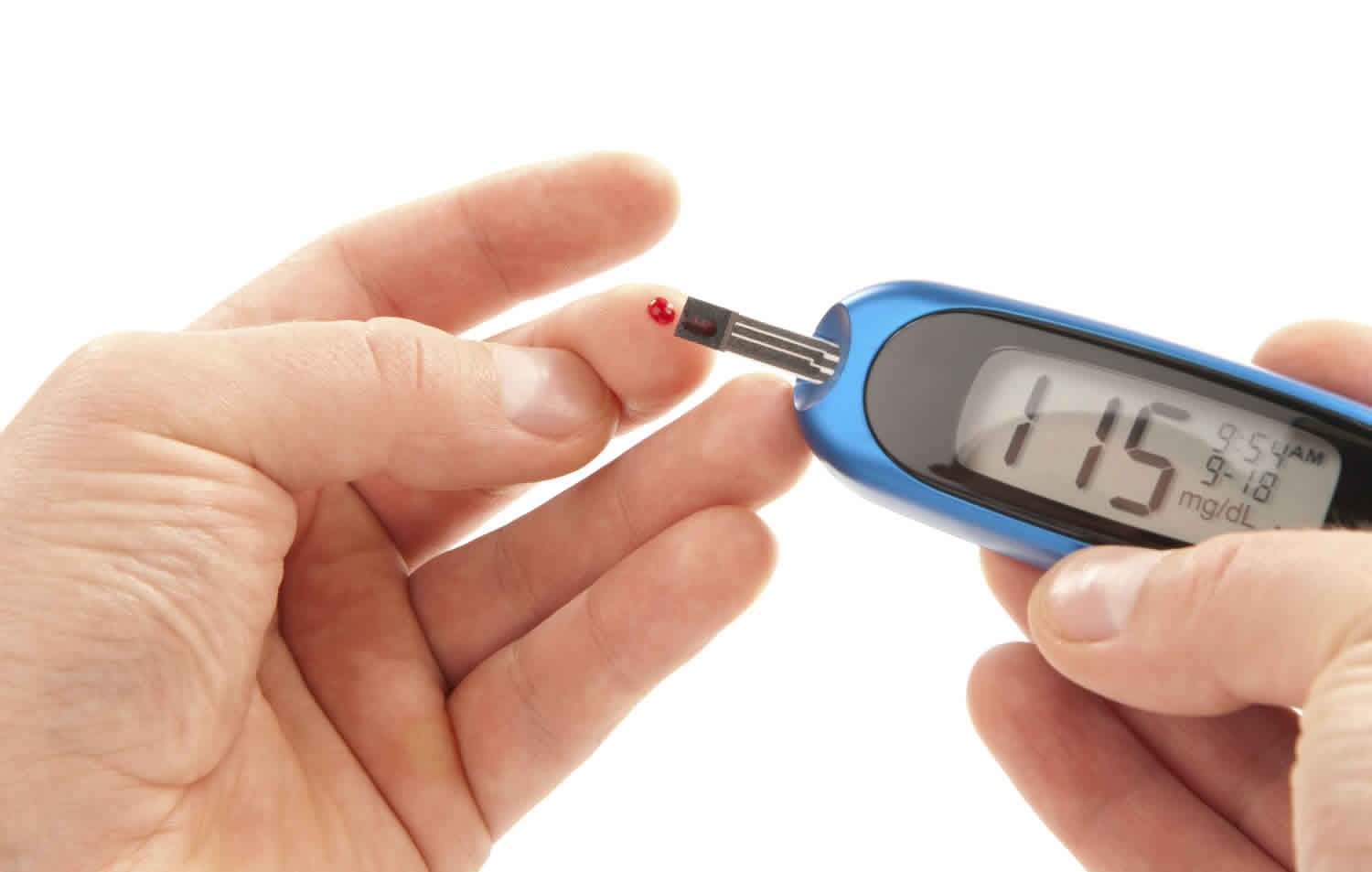
What is post prandial
Prandial means eating of food. Post prandial means after eating food.
What is normal post prandial blood sugar
A post-prandial plasma glucose test is a blood test that measures your blood glucose levels following a meal containing a set amount of carbohydrate.
Postprandial plasma glucose tests show how tolerant your body is to glucose.
- Blood glucose levels are the amount of glucose in the blood and normal blood glucose levels range from between 72 – 140.4 mg/dl (4-7.8 mmol/L). Blood glucose levels are often higher after eating and lower first thing in the morning. At least 90 minutes after meals (post prandial) under 140.4 mg/dl (<7.8 mmol/L)
- WHO (World Health Organization) indicates that impaired glucose tolerance (prediabetes) may be present if people have blood glucose greater than 140.4 mg/dl (7.8 mmol/L) but less than 200 mg/dl (11.1 mmol/L) after a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test OGTT (see below).
- Diabetes is diagnosed at blood glucose of greater than or equal to 200 mg/dl (11.1 mmol/L)
A more rigorous test, the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) may be used instead for diagnostic purposes of glucose intolerance (prediabetes), type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (also called the OGTT)
The OGTT is a two-hour test that checks your blood glucose levels before and 2 hours after you drink a special sweet drink. It tells the doctor how your body processes glucose.
- Normal OGTT: less than 140 mg/dl (<7.8 mmol/L)
- Prediabetes OGTT: 140 mg/dl to 199 mg/dl (7.8 to 11.1 mmol/L)
- Diabetes OGTT: 200 mg/dl or higher (>11.1 mmol/L)
Fasting Plasma Glucose
This test checks your fasting blood glucose levels. Fasting means after not having anything to eat or drink (except water) for at least 8 hours before the test. This test is usually done first thing in the morning, before breakfast.
- Normal fasting blood glucose levels: less than 100 mg/dl (5.6 mmol/L)
- Prediabetes fasting blood glucose levels: 100 mg/dl to 125 mg/dl (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L)
- Diabetes fasting blood glucose levels: fasting blood glucose of greater than or equal to 126 mg/dl (7.0 mmol/L)
HbA1c test
An HbA1c test does not directly measure the level of blood glucose, however, the result of the test is influenced by how high or low your blood glucose levels have tended to be over a period of 2 to 3 months.
Indications of diabetes or prediabetes are given under the following conditions:
- Normal HbA1c: Below 6.0% (42 mmol/mol)
- Prediabetes HbA1c: 6.0 to 6.4% (42 to 47 mmol/mol)
- Diabetes HbA1c: 6.5% or over (48 mmol/mol)
When are the best times of the day to check blood glucose?
Many people check blood glucose first thing in the morning before other meals. You also may want to check 2 hours after the start of a meal called “post-prandial” when you blood glucose is likely to be higher. Other times to check include:
- When you’re having symptoms of high or low blood glucose
- When you’re ill, especially if you’re unable to keep food down
- Before, during, and after physical activity
- Before you drive
- Before you go to sleep
Factors that affect your blood glucose levels
Many factors can affect your blood glucose levels. Learning about these factors can help you avoid wide swings in your levels.
What can make my blood glucose rise?
- A meal or snack
- Inactivity
- Not enough diabetes medication
- Side effects of other medications
- Infections or other illness
- Changes in hormone levels, such as during menstrual periods
- Stress
What can make my blood glucose fall?
- A meal or snack with less food or fewer carbs than usual
- Drinking alcoholic beverages, especially on an empty stomach
- Missing a meal or snack
- Extra activity
- Too much diabetes medication
- Side effects of other medications
How often do I need to check?
If you’re using your blood glucose results to decide how much insulin to take, you’ll want to check several times a day. If you have type 2 diabetes, you may be able to check less often if blood glucose results are usually on target. When you make changes in you medication, activity, or meal plan, or when you are pregnant, you should check more often. Talk it over with your health care team.
How do I keep track of my results?
You can use a log book or notebook to write down your blood glucose numbers with the date and time of the check. Electronic log books or software are also avaliable to help keep track of your results. You also can use your log book to make notes about medications, physical activity, illness, low blood glucose, stress, or any other factors that affect you blood glucose levels. If your results seem out of your usual range, circle them and make notes about possible reasons. When you meet with you health care team, review your records. Together, you’ll talk about whether changes are needed in how you take care of yourself in order to reach your goals.
There are two ways to keep track of your blood glucose levels:
- Using a blood glucose meter to help you make decisions about day-to-day care
- Getting a HbA1C at least twice a year to find out your average blood glucose for the past 2 to 3 months
You can also check our print resources to print out your own copies of our blood glucose worksheets.
What is prediabetes?
Before people develop type 2 diabetes, they almost always have “prediabetes” — blood glucose levels that are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes.
Doctors sometimes refer to prediabetes as impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) or impaired fasting glucose (IFG), depending on what test was used when it was detected. This condition puts you at a higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
There are no clear symptoms of prediabetes, so, you may have it and not know it.
Some people with prediabetes may have some of the symptoms of diabetes or even problems from diabetes already. You usually find out that you have prediabetes when being tested for diabetes.
If you have prediabetes, you should be checked for type 2 diabetes every one to two years.
Results indicating prediabetes are:
- A HbA1C of 5.7% – 6.4%
- Fasting blood glucose of 100 – 125 mg/dl (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L)
- An OGTT 2 hour blood glucose of 140 mg/dl – 199 mg/dl (7.8 to 11.1 mmol/L)
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
You will not develop type 2 diabetes automatically if you have prediabetes. For some people with prediabetes, early treatment can actually return blood glucose levels to the normal range.
Research shows that you can lower your risk for type 2 diabetes by 58% by:
- Losing 7% of your body weight (or 15 pounds if you weigh 200 pounds)
- Exercising moderately (such as brisk walking) 30 minutes a day, five days a week
Don’t worry if you can’t get to your ideal body weight. Losing even 10 to 15 pounds can make a huge difference.