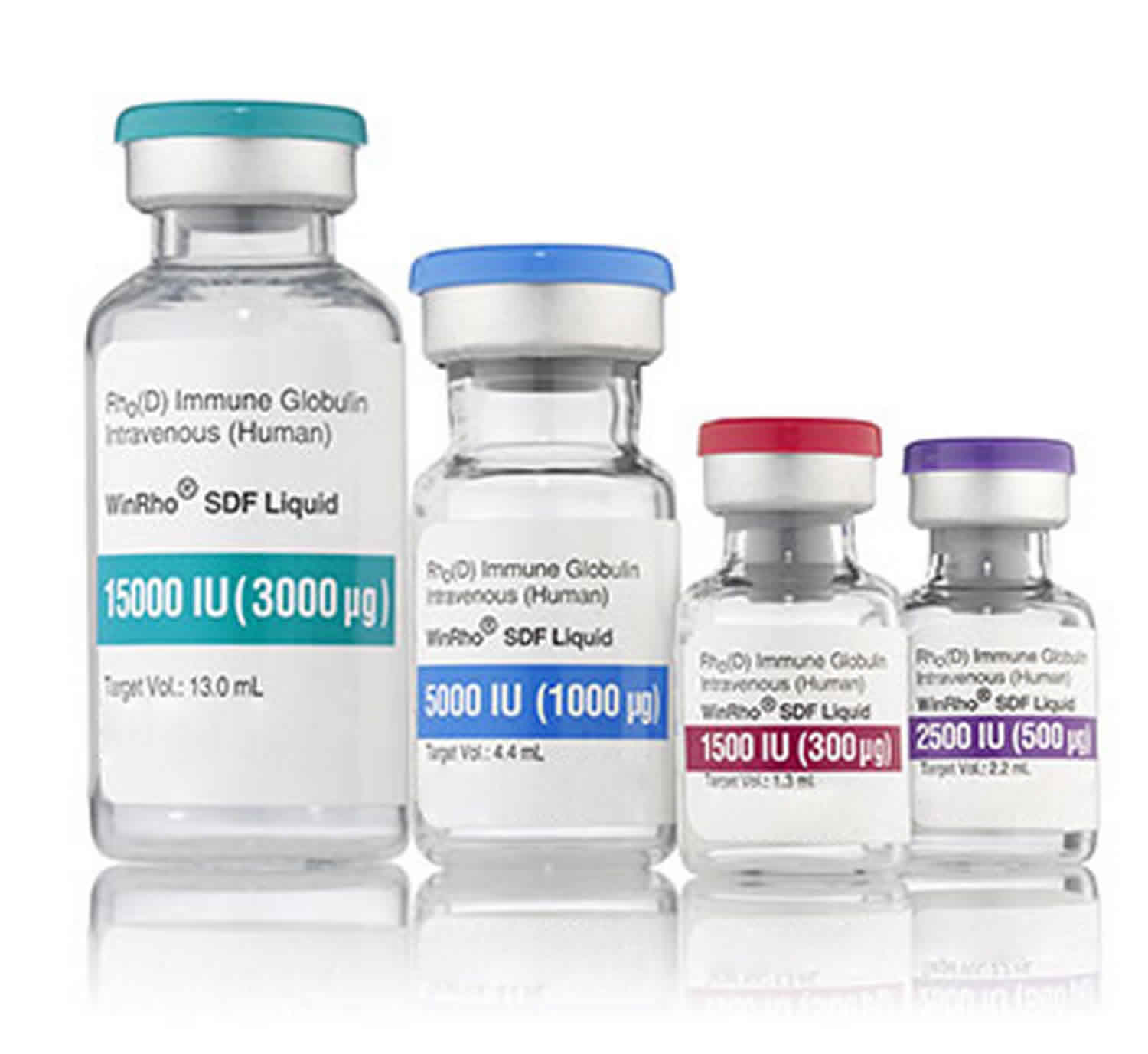
Rho D immune globulin
Rho D immune globulin or Rho (D) immune globulin is used to treat immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) in patients with Rh-positive blood. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura is a type of blood disorder where the person has a very low number of platelets. Platelets help to clot the blood. Rho D immune globulin is also used to prevent antibodies from forming after a person with Rh-negative blood receives a transfusion with Rh-positive blood, or during pregnancy when a mother has Rh-negative blood and the baby is Rh-positive. Rho D immune globulin belongs to a group of medicines called immunizing agents. Rho D immune globulin is a sterilized solution made from human blood. Rho D immune globulin works to boost the immune system and prevent excessive bleeding.
The Rh factor is one part of the red blood cell. A person has either Rh-positive or Rh-negative blood. If you receive the opposite type of blood, your body will create antibodies that can destroy the red blood cells. A person who is Rh negative can be exposed to Rh positive blood through a mismatched blood transfusion or during pregnancy when the baby has the opposite blood type. When a pregnant woman is Rh-negative and her baby is Rh-positive, the baby’s blood can get into her system and cause her to make antibodies that will try to destroy the Rh positive blood cells. When the same woman has a second baby with Rh-positive blood, the antibodies will destroy the red blood cells in the baby. This can cause medical problems such as anemia (low red blood cells), kidney failure, or shock. Rho D immune globulin is given to these women during pregnancy or after delivery to prevent them from making antibodies.
Rho D immune globulin is often used during and after pregnancy. Rho D immune globulin is not known to be harmful to a baby during pregnancy or while breast-feeding.
Rho D immune globulin is to be administered only by or under the supervision of your doctor. A nurse or other trained health professional will give you Rho D immune globulin in a hospital. Rho D immune globulin is given through a needle placed in one of your veins or as a shot into one of your muscles.
Rho D immune globulin is made from donated human blood. Some human blood products have transmitted certain viruses to people who have received them. The risk of getting a virus from medicines made from human blood has been greatly reduced in recent years. This is the result of required testing of human donors for certain viruses, and testing during the making of Rho D immune globulin. Although the risk is low, talk with your doctor if you have concerns.
Rho D immune globulin may cause serious types of allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. Tell your doctor right away if you or your child have itching, a rash, hives, chest pain, dizziness or lightheadedness, trouble breathing, or any swelling of your hands, face, or mouth after you receive this medicine.
Rho D immune globulin may cause blood clots, especially in patients with a history of blood clotting problems, heart disease, and atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) or circulation problems. Patients who stay in bed for a long time because of surgery or illness may also have blood clots. Check with your doctor right away if you or your child suddenly have chest pain, shortness of breath, a severe headache, leg pain, or problems with vision, speech, or walking.
Rho D immune globulin may cause a rare and serious lung problem a few hours after it is given. Tell your doctor right away if you or your child have any breathing problems with or without a fever after you receive the medicine.
While you are being treated with Rho D immune globulin, do not have any immunizations (vaccines) without your doctor’s approval. Live virus vaccines should not be given for 3 months after receiving Rho D immune globulin.
Rho D immune globulin important information
You should not receive Rho D immune globulin if you have immune globulin A (IgA) deficiency with antibody to IgA, or if you have hemolytic anemia (a lack of red blood cells).
Rho D immune globulin can cause an abnormal breakdown of red blood cells. This effect can lead to life-threatening blood clots or organ failure.
Call your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms: fever, chills, back pain, unusual weakness, red or pink urine, pale skin, feeling short of breath, little or no urinating, rapid weight gain, sudden numbness or weakness, slurred speech, problems with vision or balance, coughing up blood, or swelling or warmth in your leg.
Rho D immune globulin special precautions
Before taking Rho D immune globulin
You should not receive this medicine if you have ever had an allergic reaction to an immune globulin, or if you have:
- immune globulin A (IgA) deficiency with antibody to IgA; or
- hemolytic anemia (a lack of red blood cells).
To make sure Rho D immune globulin is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have:
- a history of anemia;
- heart disease or a history of coronary artery disease (hardened arteries);
- a bleeding disorder (such as hemophilia);
- high triglycerides (a type of fat in the blood);
- kidney disease; or
- diabetes.
If you are receiving Rho D immune globulin to treat a mismatched blood transfusion, tell your doctor if you are pregnant or if you ever plan to become pregnant.
If you are an Rh-negative woman and you become pregnant, you must tell your doctor if you have ever been exposed to Rh-positive blood in your lifetime. This includes exposure from a mismatched blood transfusion, or exposure during your first pregnancy. Your history of exposure and treatment will be extremely important to each and every one of your pregnancies.
Rho D immune globulin is made from human plasma (part of the blood) which may contain viruses and other infectious agents. Donated plasma is tested and treated to reduce the risk of it containing infectious agents, but there is still a small possibility it could transmit disease. Talk with your doctor about the risks and benefits of using this medication.
Allergies
Tell your doctor if you have ever had any unusual or allergic reaction to this medicine or any other medicines. Also tell your health care professional if you have any other types of allergies, such as to foods, dyes, preservatives, or animals. For non-prescription products, read the label or package ingredients carefully.
Pediatric
Appropriate studies performed to date have not demonstrated pediatric-specific problems that would limit the usefulness of Rho D immune globulin in children. It is not recommended for an infant with Rh-positive blood whose mother is Rh-negative.
Geriatric
Although appropriate studies on the relationship of age to the effects of Rho D immune globulin have not been performed in the geriatric population, geriatric-specific problems are not expected to limit the usefulness of Rho D immune globulin in the elderly. However, elderly patients are more likely to have age-related heart, kidney, or liver problems, and might have conditions that require an adjustment in the dose for patients receiving Rho D immune globulin.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C: Animal studies have shown an adverse effect and there are no adequate studies in pregnant women OR no animal studies have been conducted and there are no adequate studies in pregnant women.
Rho D immune globulin drug interactions
Although certain medicines should not be used together at all, in other cases two different medicines may be used together even if an interaction might occur. In these cases, your doctor may want to change the dose, or other precautions may be necessary. Tell your healthcare professional if you are taking any other prescription or nonprescription (over-the-counter [OTC]) medicine.
Other interactions
Certain medicines should not be used at or around the time of eating food or eating certain types of food since interactions may occur. Using alcohol or tobacco with certain medicines may also cause interactions to occur. Discuss with your healthcare professional the use of your medicine with food, alcohol, or tobacco.
Other medical problems
The presence of other medical problems may affect the use of Rho D immune globulin. Make sure you tell your doctor if you have any other medical problems, especially:
- Anemia, severe or
- Blood clotting problems, history of or
- Breathing problems, severe or
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (blood clotting problem) or
- Kidney problems or
- Pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs), history of—Use with caution. May make these conditions worse.
- Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), history of or
- Heart or blood vessel problems or
- Hyperviscosity (thick blood), history of or
- Stroke—Use with caution. May cause side effects to become worse.
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (bleeding problem) or
- Hemolysis, active (red blood cells are being destroyed) or
- Immunoglobulin A (IgA) deficiency with antibodies against IgA—Should not be used in patients with these conditions.
- Diabetes—The liquid form of WinRho® contains maltose. Some glucose testing systems will not work properly if maltose is in the blood. Discuss this with your doctor.
Rho D immune globulin dose
Rho D immune globulin is injected into a muscle or a vein. You will receive this injection in a clinic or hospital setting. Your breathing, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and other vital signs will be watched closely after you receive immune globulin. Your urine may also need to be tested every 2 to 4 hours for at least 8 hours.
For treatment during pregnancy, Rho D immune globulin is usually given at regular intervals during the last half of the pregnancy, and again after the baby is born.
For treatment of a mismatched blood transfusion, the medicine is given when symptoms of an immune response appear (when the body starts making Rh antibodies).
To be sure this medicine is helping your condition, you may need frequent blood tests. You may not notice any change in your symptoms, but your blood work will help your doctor determine how long to treat you with Rho D immune globulin.
Rho D immune globulin can cause false results with certain lab tests for glucose (sugar) in the blood. Tell any doctor who treats you that you are using this medicine.
Injection procedure
DO NOT INJECT INTRAVENOUSLY. DO NOT INJECT NEONATE. HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose (1500 IU; 300 mcg) is administered intramuscularly, preferably in the deltoid muscle of the upper arm or lateral thigh muscle. The gluteal region should not be used as an injection site because of the risk of injury to the sciatic nerve 1.
- Single Syringe Dose: INJECT ENTIRE CONTENTS OF THE SYRINGE INTO THE INDIVIDUAL INTRAMUSCULARLY.
- Multiple Syringe Dose: Calculate the number of syringes of HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose (1500 IU; 300 mcg) to be given (see below section). The total volume of HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose (1500 IU; 300 mcg) can be given in divided doses at different sites at one time or the total dose may be divided and injected at intervals, provided the total dosage is given within 72 hours of the fetomaternal hemorrhage or transfusion. USING STERILE TECHNIQUE, INJECT THE ENTIRE CONTENTS OF THE CALCULATED NUMBER OF SYRINGES INTRAMUSCULARLY INTO THE PATIENT.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose (1500 IU; 300 mcg) is supplied with a syringe and an attached UltraSafe® Needle Guard for your protection and convenience. Please follow instructions below for proper use of syringe and UltraSafe® Needle Guard.
Pregnancy and Other Obstetric Conditions
- For postpartum prophylaxis, administer one syringe of HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose (1500 IU; 300 mcg), preferably within 72 hours of delivery. Although a lesser degree of protection is afforded if Rh antibody is administered beyond the 72-hour period, HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose may still be given 2. Full-term deliveries can vary in their dosage requirements depending on the magnitude of the fetomaternal hemorrhage. One full dose syringe of HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose provides sufficient antibody to prevent Rh sensitization if the volume of red blood cells that has entered the circulation is 15 mL or less 3. In instances where a large (greater than 30 mL of whole blood or 15 mL red blood cells) fetomaternal hemorrhage is suspected, a fetal red cell count by an approved laboratory technique (e.g., modified Kleihauer-Betke acid elution stain technique) should be performed to determine the dosage of immune globulin required 2. The red blood cell volume of the calculated fetomaternal hemorrhage is divided by 15 mL to obtain the number of syringes of HyperRHO S/D Full Dose (1500 IU; 300 mcg) for administration 2. If more than 15 mL of red cells is suspected or if the dose calculation results in a fraction, administer the next higher whole number of syringes (e.g., if 1.4, give 2 syringes).
- For antenatal prophylaxis, one full dose syringe of HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose (1500 IU; 300 mcg) is administered at approximately 28 weeks’ gestation. This must be followed by another full dose (1500 IU; 300 mcg) , preferably within 72 hours following delivery, if the infant is Rh positive.
- Following threatened abortion at any stage of gestation with continuation of pregnancy, it is recommended that a full dose of HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose (1500 IU; 300 mcg) be given. If more than 15 mL of red cells is suspected due to fetomaternal hemorrhage, the same dose modification in No. 1 above applies.
- Following miscarriage, abortion, or termination of ectopic pregnancy at or beyond 13 weeks’ gestation, it is recommended that a HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose (1500 IU; 300 mcg) be given. If more than 15 mL of red cells is suspected due to fetomaternal hemorrhage, the same dose modification in No. 1 above applies. If pregnancy is terminated prior to 13 weeks’ gestation, where licensed, a single dose of HyperRHO® Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Mini-Dose (250 IU; 50mcg) may be used instead of HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose (1500 IU; 300 mcg).
- Following amniocentesis at either 15 to 18 weeks’ gestation or during the third trimester, or following abdominal trauma in the second or third trimester, it is recommended that a HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose (1500 IU; 300 mcg) be administered. If there is a fetomaternal hemorrhage in excess of 15 mL of red cells, the same dose modification in No. 1 applies.
If abdominal trauma, amniocentesis, or other adverse event requires the administration of HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose (1500 IU; 300 mcg) at 13 to 18 weeks’ gestation, another full dose should be given at 26 to 28 weeks. To maintain protection throughout pregnancy, the level of passively acquired anti-Rho D should not be allowed to fall below the level required to prevent an immune response to Rh positive red cells. The half-life of IgG is 23 to 26 days. In any case, a HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose should be given within 72 hours after delivery if the baby is Rh positive. If delivery occurs within 3 weeks after the last dose, the postpartum dose may be withheld unless there is a fetomaternal hemorrhage in excess of 15 mL of red blood cells 4.
Transfusion
In the case of a transfusion of Rho D positive red cells to an Rho D negative recipient, the volume of Rh positive whole blood administered is multiplied by the hematocrit of the donor unit giving the volume of red blood cells transfused. The volume of red blood cells is divided by 15 mL which provides the number of syringes of HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose to be administered.
If the dose calculated results in a fraction, the next higher whole number of syringes should be administered (e.g., if 1.4, give 2 syringes). HyperRHO Solvent/Detergent Treated Preservative-free Full Dose should be administered within 72 hours after an incompatible transfusion, but preferably as soon as possible.
Rho D immune globulin side effects
Check with your doctor or nurse immediately if any of the following side effects occur:
Rare side effects
- bloody urine
- decreased frequency of urination or amount of urine
- fever
- increased blood pressure
- increased thirst
- loss of appetite
- lower back pain
- nausea or vomiting
- pale skin
- swelling of the face, fingers, or lower legs
- troubled breathing
- unusual bleeding or bruising
- unusual tiredness or weakness
- weight gain
Some side effects may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. Check with your health care professional if any of the following side effects continue or are bothersome or if you have any questions about them:
Less common
- Soreness at the place of injection
Other side effects not listed may also occur in some patients. If you notice any other effects, check with your healthcare professional. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
References- Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) and the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP): General recommendations on immunization. MMWR 2002: 51(RR02), 1-36.
- Current uses of Rho immune globulin and detection of antibodies. ACOG Tech Bull 35, 1976.
- Rho(D) immune globulin (human). Med Lett Drugs Ther 16(1):3-4, 1974.
- Garraty G (ed.): Hemolytic disease of the newborn. Arlington, VA, American Association of Blood Banks, 1984, p 78.