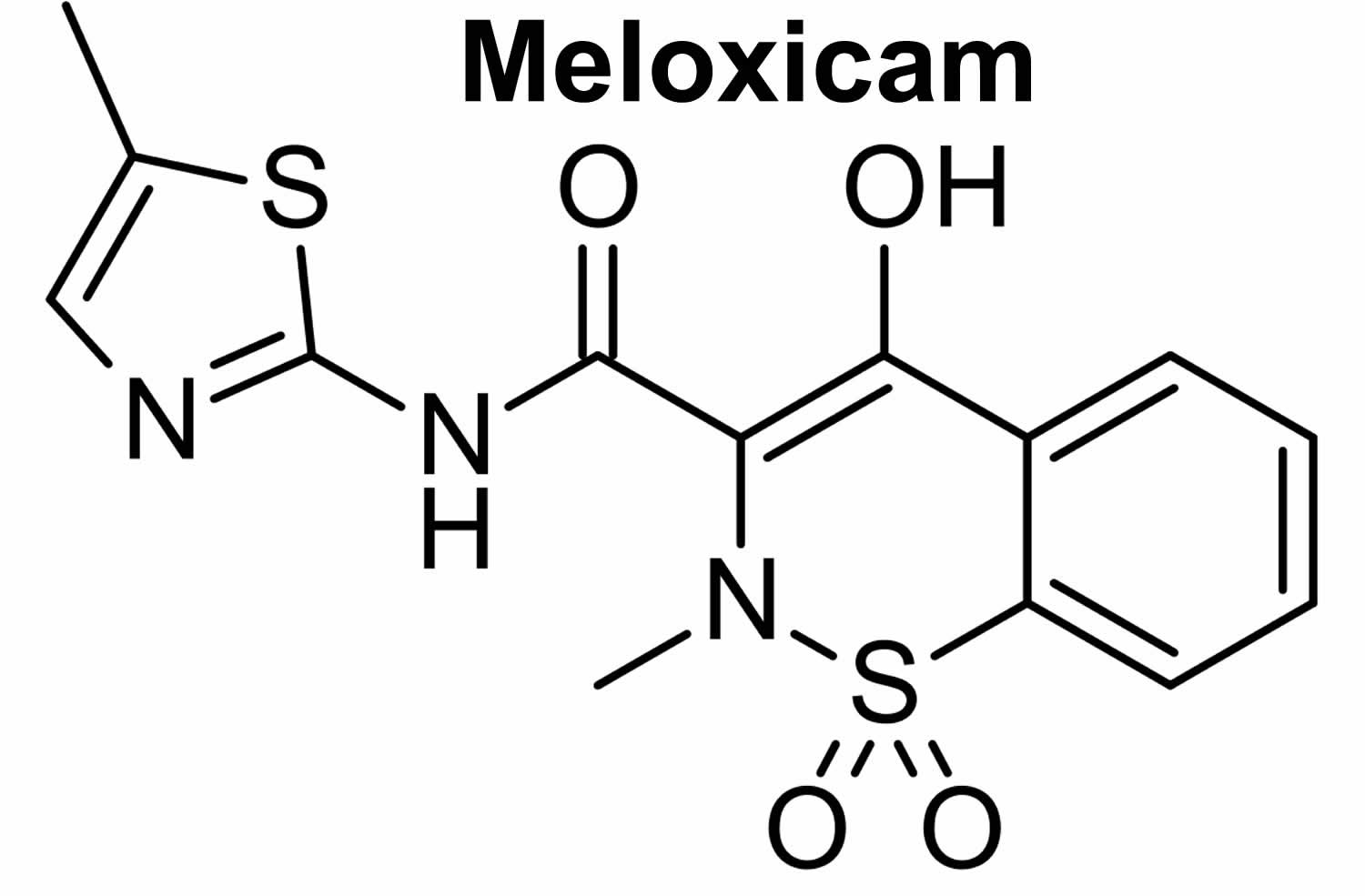
What is meloxicam
Meloxicam is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, tenderness, swelling, and stiffness caused by osteoarthritis (arthritis caused by a breakdown of the lining of the joints) and rheumatoid arthritis (arthritis caused by swelling of the lining of the joints). Meloxicam is also used to relieve the pain, tenderness, swelling, and stiffness caused by juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (a type of arthritis that affects children) in children 2 years of age and older. Meloxicam works by stopping the body’s production of a substance that causes pain, fever, and inflammation. However, meloxicam does not cure arthritis and will only help you as long as you continue to take it.
Meloxicam is available only with your doctor’s prescription.
Meloxicam is available in the following dosage forms:
- Capsule
- Tablet
- Suspension
Meloxicam contraindications
Meloxicam is contraindicated in the following patients:
- Known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reactions and serious skin reactions) to Meloxicam or any components of the drug product
- History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients
- In the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery
RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
People who take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (other than aspirin) such as meloxicam may have a higher risk of having a heart attack, or a stroke than people who do not take these medications. These events may happen without warning and may cause death. This risk may be higher for people who take NSAIDs for a long time. Do not take an NSAID such as meloxicam if you have recently had a heart attack, unless directed to do so by your doctor. Tell your doctor if you or anyone in your family has or has ever had heart disease, a heart attack, a stroke, if you smoke, and if you have or have ever had high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or diabetes. Get emergency medical help right away if you experience any of the following symptoms: chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness in one part or side of the body, or slurred speech.
If you will be undergoing a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG; a type of heart surgery), you should not take meloxicam right before or right after the surgery.
NSAIDs such as meloxicam may cause ulcers, bleeding, or holes in the stomach or intestine. These problems may develop at any time during treatment, may happen without warning symptoms, and may cause death. The risk may be higher for people who take NSAIDs for a long time, are older in age, have poor health, or drink large amounts of alcohol while taking meloxicam. Tell your doctor if you take any of the following medications: anticoagulants (‘blood thinners’) such as warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven); aspirin; other NSAIDs such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn); oral steroids such as dexamethasone, methylprednisolone (Medrol), and prednisone (Rayos); selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as citalopram (Celexa), fluoxetine (Prozac, Sarafem, Selfemra, in Symbyax), fluvoxamine (Luvox), paroxetine (Brisdelle, Paxil, Pexeva), and sertraline (Zoloft); or serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) such as desvenlafaxine (Khedezla, Pristiq), duloxetine (Cymbalta), and venlafaxine (Effexor XR). Also tell your doctor if you have or have ever had ulcers or bleeding in your stomach or intestines, or other bleeding disorders. If you experience any of the following symptoms, stop taking meloxicam and call your doctor: stomach pain, heartburn, vomit that is bloody or looks like coffee grounds, blood in the stool, or black and tarry stools.
Keep all appointments with your doctor and the laboratory. Your doctor will monitor your symptoms carefully and will probably order certain tests to check your body’s response to meloxicam. Be sure to tell your doctor how you are feeling so that your doctor can prescribe the right amount of medication to treat your condition with the lowest risk of serious side effects.
Your doctor or pharmacist will give you the manufacturer’s patient information sheet (Medication Guide) when you begin treatment with meloxicam and each time you refill your prescription. Read the information carefully and ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions. You can also visit the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) website (https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm) or the manufacturer’s website to obtain the Medication Guide.
How long does it take for meloxicam to work?
The painkilling effect of meloxicam begins soon after a dose is taken, but the anti-inflammatory effect can sometimes take up to three weeks to get the best results.
Does meloxicam cause weight gain?
Meloxicam may cause congestive heart failure and edema, which can cause unexplained weight gain and shortness of breath.
How should meloxicam be used?
Meloxicam comes as a tablet and suspension (liquid) to take by mouth. It is usually taken once a day with or without food. Take meloxicam at the same time every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take meloxicam exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Shake the suspension well before each use to mix the medication evenly. Measure the dose with a marked measuring spoon, oral syringe, or medicine cup. The average household teaspoon may not hold the right amount of liquid.
For safe and effective use of meloxicam, do not take more of it, do not take it more often, and do not take it for a longer time than your doctor ordered. Taking too much of meloxicam may increase the chance of side effects.
Meloxicam should come with a Medication Guide. It is very important that you read and understand this information. Be sure to ask your doctor about anything you do not understand.
Swallow the capsule or tablet whole. Do not crush, break, or chew it.
You may take meloxicam with or without food.
Allergies
Tell your doctor if you have ever had any unusual or allergic reaction to this medicine or any other medicines. Also tell your health care professional if you have any other types of allergies, such as to foods, dyes, preservatives, or animals. For non-prescription products, read the label or package ingredients carefully.
Pediatric
Meloxicam is not approved for use by anyone younger than 2 years old.
Appropriate studies performed to date have not demonstrated pediatric-specific problems that would limit the usefulness of meloxicam oral liquid or tablets in children with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis 2 years of age and older.
Appropriate studies have not been performed on the relationship of age to the effects of meloxicam capsules in the pediatric population. Safety and efficacy have not been established.
Geriatric
Appropriate studies performed to date have not demonstrated geriatric-specific problems that would limit the usefulness of meloxicam in the elderly. However, elderly patients are more likely to have serious stomach, heart, or kidney problems, which may require caution and an adjustment in the dose for patients receiving this medicine.
Meloxicam special precautions
Before taking meloxicam:
- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to meloxicam, sorbitol, aspirin or other NSAIDs such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn),any other medications, or any of the ingredients in meloxicam tablets and suspension. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of the ingredients.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you are taking or plan to take. Be sure to mention the medications listed in the IMPORTANT WARNING section and any of the following: angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors such as benazepril (Lotensin, in Lotrel), captopril , enalapril (Vasotec, in Vaseretic), fosinopril, lisinopril (in Zestoretic), and quinapril (Accupril, in Accuretic, in Quinaretic); angiotensin receptor blockers such as azilsartan (Edarbi, in Edarbyclor), candesartan (Atacand, in Atacand HCT), eprosartan (Teveten), irbesartan (Avapro, in Avalide), losartan (Cozaar, in Hyzaar), olmesartan (Benicar, in Azor, in Benicar HCT, in Tribenzor), telmisartan (Micardis, in Micardis HCT, in Twynsta); beta blockers such as atenolol (Tenormin, in Tenoretic), labetalol (Trandate), metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol XL, in Dutoprol), nadolol (Corgard, in Corzide), and propranolol (Hemangeol, Inderal, Innopran); cholestyramine (Prevalite); cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune); diuretics (‘water pills’); lithium (Lithobid); methotrexate (Otrexup, Rasuvo, Trexall); pemetrexed (Alimta); and sodium polystyrene sulfonate products (Kayexalate). Your doctor may need to change the doses of your medications or monitor you carefully for side effects.
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had asthma, especially if you have frequent stuffed or runny nose or nasal polyps (swelling of the lining of the nose); heart failure; swelling of the hands, feet, ankles, or lower legs; or kidney or liver disease.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, especially if you are in the last few months of your pregnancy, you plan to become pregnant, or you are breastfeeding. If you become pregnant while taking meloxicam, call your doctor.
- if you are having surgery, including dental surgery, tell the doctor or dentist that you are taking meloxicam.
- if you have fructose intolerance (an inherited condition in which the body lacks the protein needed to break down fructose [a fruit sugar found in certain sweeteners such as sorbitol]), you should know that the oral suspension is sweetened with sorbitol. Tell your doctor if you have fructose intolerance.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Taking meloxicam during the last 3 months of pregnancy may harm the unborn baby. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
Meloxicam may cause a delay in ovulation (the release of an egg from an ovary). You should not take this medicine if you are undergoing fertility treatment, or are otherwise trying to get pregnant.
Breastfeeding
Meloxicam can pass into breast milk and may harm a nursing baby. There are no adequate studies in women for determining infant risk when using this medication during breastfeeding. Weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks before taking this medication while breastfeeding.
Meloxicam drug interactions
Although certain medicines should not be used together at all, in other cases two different medicines may be used together even if an interaction might occur. In these cases, your doctor may want to change the dose, or other precautions may be necessary. When you are taking this medicine, it is especially important that your healthcare professional know if you are taking any of the medicines listed below. The following interactions have been selected on the basis of their potential significance and are not necessarily all-inclusive.
Using meloxicam with any of the following medicines is not recommended. Your doctor may decide not to treat you with this medication or change some of the other medicines you take.
- Ketorolac
Using meloxicam with any of the following medicines is usually not recommended, but may be required in some cases. If both medicines are prescribed together, your doctor may change the dose or how often you use one or both of the medicines.
- Abciximab
- Aceclofenac
- Acemetacin
- Acenocoumarol
- Amiloride
- Amineptine
- Amitriptyline
- Amitriptylinoxide
- Amoxapine
- Amtolmetin Guacil
- Anagrelide
- Apixaban
- Ardeparin
- Argatroban
- Aspirin
- Balsalazide
- Bemiparin
- Bendroflumethiazide
- Benzthiazide
- Beta Glucan
- Betamethasone
- Bismuth Subsalicylate
- Bivalirudin
- Bromfenac
- Budesonide
- Bufexamac
- Bumetanide
- Cangrelor
- Celecoxib
- Ceritinib
- Certoparin
- Chlorothiazide
- Chlorthalidone
- Choline Magnesium Trisalicylate
- Choline Salicylate
- Cilostazol
- Citalopram
- Clomipramine
- Clonixin
- Clopamide
- Clopidogrel
- Cortisone
- Cyclopenthiazide
- Cyclosporine
- Dabigatran Etexilate
- Dalteparin
- Danaparoid
- Deflazacort
- Desipramine
- Desirudin
- Desvenlafaxine
- Dexamethasone
- Dexibuprofen
- Dexketoprofen
- Diazoxide
- Dibenzepin
- Diclofenac
- Diflunisal
- Digoxin
- Dipyridamole
- Dipyrone
- Dothiepin
- Doxepin
- Droxicam
- Duloxetine
- Edoxaban
- Enoxaparin
- Eplerenone
- Epoprostenol
- Eptifibatide
- Escitalopram
- Ethacrynic Acid
- Etodolac
- Etofenamate
- Etoricoxib
- Felbinac
- Fenoprofen
- Fepradinol
- Feprazone
- Feverfew
- Floctafenine
- Flufenamic Acid
- Fluocortolone
- Fluoxetine
- Flurbiprofen
- Fluvoxamine
- Fondaparinux
- Furosemide
- Ginkgo
- Gossypol
- Heparin
- Hydrochlorothiazide
- Hydrocortisone
- Hydroflumethiazide
- Ibuprofen
- Iloprost
- Imipramine
- Indapamide
- Indomethacin
- Ketoprofen
- Lepirudin
- Levomilnacipran
- Lithium
- Lofepramine
- Lornoxicam
- Loxoprofen
- Lumiracoxib
- Magnesium Salicylate
- Meadowsweet
- Meclofenamate
- Mefenamic Acid
- Melitracen
- Meloxicam
- Mesalamine
- Methotrexate
- Methyclothiazide
- Methylprednisolone
- Metolazone
- Milnacipran
- Morniflumate
- Nabumetone
- Nadroparin
- Naproxen
- Nefazodone
- Nepafenac
- Niflumic Acid
- Nimesulide
- Nimesulide Beta Cyclodextrin
- Nortriptyline
- Olsalazine
- Opipramol
- Oxaprozin
- Oxyphenbutazone
- Paramethasone
- Parecoxib
- Parnaparin
- Paroxetine
- Pemetrexed
- Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium
- Pentoxifylline
- Phenindione
- Phenprocoumon
- Phenylbutazone
- Phenyl Salicylate
- Piketoprofen
- Piroxicam
- Polythiazide
- Pralatrexate
- Prasugrel
- Prednisolone
- Prednisone
- Proglumetacin
- Propyphenazone
- Proquazone
- Protein C
- Protriptyline
- Reboxetine
- Reviparin
- Rivaroxaban
- Rofecoxib
- Salicylamide
- Salicylic Acid
- Salsalate
- Sertraline
- Sibutramine
- Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate
- Sodium Salicylate
- Spironolactone
- Sulfasalazine
- Sulindac
- Tacrolimus
- Tenoxicam
- Tianeptine
- Tiaprofenic Acid
- Ticagrelor
- Ticlopidine
- Tinzaparin
- Tirofiban
- Tolfenamic Acid
- Tolmetin
- Torsemide
- Treprostinil
- Triamterene
- Trichlormethiazide
- Trimipramine
- Trolamine Salicylate
- Valdecoxib
- Venlafaxine
- Vilazodone
- Vorapaxar
- Vortioxetine
- Warfarin
- Xipamide
Using meloxicam with any of the following medicines may cause an increased risk of certain side effects, but using both drugs may be the best treatment for you. If both medicines are prescribed together, your doctor may change the dose or how often you use one or both of the medicines.
- Acebutolol
- Alacepril
- Atenolol
- Azilsartan
- Azilsartan Medoxomil
- Benazepril
- Betaxolol
- Bisoprolol
- Candesartan
- Captopril
- Carteolol
- Carvedilol
- Celiprolol
- Cholestyramine
- Cilazapril
- Delapril
- Enalapril
- Enalaprilat
- Eprosartan
- Esmolol
- Fosinopril
- Imidapril
- Irbesartan
- Itraconazole
- Labetalol
- Levobunolol
- Lisinopril
- Losartan
- Metipranolol
- Metoprolol
- Moexipril
- Nadolol
- Nebivolol
- Olmesartan
- Oxprenolol
- Penbutolol
- Pentopril
- Perindopril
- Pindolol
- Practolol
- Propranolol
- Quinapril
- Ramipril
- Sotalol
- Spirapril
- Telmisartan
- Temocapril
- Timolol
- Trandolapril
- Valsartan
- Voriconazole
- Zofenopril
Other Interactions
Certain medicines should not be used at or around the time of eating food or eating certain types of food since interactions may occur. Using alcohol or tobacco with certain medicines may also cause interactions to occur. Discuss with your healthcare professional the use of your medicine with food, alcohol, or tobacco.
What does meloxicam do
Meloxicam is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the oxicam class which acts by inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis, thereby exerting anti-inflammatory, analgesic and anti-pyretic properties 1. The enzyme inhibited by NSAID is the COX (cyclooxygenase) enzyme. The COX enzyme exists in two isoforms: COX-1 and COX-2. COX-1 (cyclooxygenase-1) is primarily responsible for synthesis of prostaglandins important for maintaining a healthy gastrointestinal tract, renal function, platelet function, and other normal functions. COX-2 (cyclooxygenase-2) is induced and responsible for synthesizing prostaglandins that are important mediators of pain, inflammation, and fever. However, it is known that there is some crossover of COX-1 and COX-2 effects, and COX-2 activity is important for some biological effects. Meloxicam preferentially inhibits the COX-2 (cyclooxygenase-2) isoenzyme and has been shown to be safer than non-selective NSAIDs like aspirin, flunixin and ketoprofen 2. Meloxicam is relatively COX-1 sparing compared to older NSAIDs, but it is not known if the specificity for COX-1 or COX-2 is related to efficacy or safety.
What is meloxicam used for
Meloxicam is an nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to relieve the symptoms of arthritis (juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis), such as inflammation, swelling, stiffness, and joint pain.
Meloxicam is used to treat pain or inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis in adults.
Meloxicam is also used to treat juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in children who are at least 2 years old.
Meloxicam is also used sometimes to treat ankylosing spondylitis (arthritis that mainly affects the spine). Talk to your doctor about the possible risks of using meloxicam for your condition.
Meloxicam may be prescribed for other uses; ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
Meloxicam dosage
The dose of this medicine will be different for different patients. Follow your doctor’s orders or the directions on the label. The following information includes only the average doses of this medicine. If your dose is different, do not change it unless your doctor tells you to do so.
The amount of medicine that you take depends on the strength of the medicine. Also, the number of doses you take each day, the time allowed between doses, and the length of time you take the medicine depend on the medical problem for which you are using the medicine.
For oral dosage form (capsules):
- For osteoarthritis:
- Adults—At first, 5 milligrams (mg) once a day. Your doctor may increase your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 10 mg per day.
- Children—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor.
For oral dosage forms (suspension or tablets):
- For juvenile rheumatoid arthritis:
- Children 2 years of age and older—Dose is based on body weight and must be determined by your doctor. The dose is 0.125 milligram (mg) per kilogram (kg) of body weight once a day. Your doctor may increase the dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 7.5 mg once a day.
- Children younger than 2 years of age—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor.
- For osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis:
- Adults—At first, 7.5 milligrams (mg) once a day. Your doctor may increase your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 15 mg once a day.
- Children—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor.
Adult Dose for Osteoarthritis
- Use: For the relief of signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis pain
Oral Suspension and Tablets:
- Initial dose: 7.5 mg orally once a day
- Maintenance dose: 15 mg orally once a day in patients requiring additional analgesia
- Maximum dose: 15 mg orally once a day
Oral Capsules:
- Initial dose: 5 mg orally once a day
- Maintenance dose: 10 mg orally once a day in patients requiring additional analgesia
- Maximum dose: 10 mg orally once a day
Comments:
- Oral capsules are not interchangeable with the suspension/tablets even if the total milligram strength is the same and should therefore, not be substituted.
- The lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible consistent with individual treatment goals should be used.
Adult Dose for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Use: For the relief of signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis
Oral Suspension and Tablets:
- Initial dose: 7.5 mg orally once a day
- Maintenance dose: 15 mg orally once a day in patients requiring additional analgesia
- Maximum dose: 15 mg orally once a day
Comment:
- The lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible consistent with individual treatment goals should be used.
Pediatric Dose for Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Use: For the relief of signs and symptoms of pauciarticular or polyarticular course juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
2 years or older:
- Oral Suspension: 0.125 mg/kg orally once a day
- Maximum dose: 7.5 mg orally once a day
Comments:
- In order to improve dosing accuracy in lower weight children, the oral suspension should be used.
- No additional benefit has been seen in doses above 0.125 mg/kg once a day.
Oral Tablets:
- 60 kg or greater: 7.5 mg orally once a day
Comments:
- The oral tablets should not be used in children who weigh less than 60 kg.
- No additional benefit has been demonstrated with doses above 7.5 mg/day.
Renal Dose Adjustments
- Mild to moderate renal dysfunction: No adjustment recommended.
- Severe renal dysfunction: Not recommended.
Liver Dose Adjustments
- Mild to moderate liver dysfunction: No adjustment recommended.
- Severe liver dysfunction: Use with caution; monitor for worsening of liver function.
What should I do if I forget a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember it. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and continue your regular dosing schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one.
Meloxicam side effects
Common meloxicam side effects may include:
- upset stomach, nausea, vomiting, heartburn;
- diarrhea, constipation, gas;
- dizziness; or
- cold symptoms, flu symptoms.
Meloxicam may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:
- diarrhea
- constipation
- gas
- sore throat
Some side effects can be serious. If you experience any of the following symptoms, call your doctor immediately. Do not take any more meloxicam until you speak to your doctor:
- fever
- blisters
- rash
- skin blisters or peeling
- hives
- itching
- swelling of the eyes, face, tongue, lips, or throat
- difficulty breathing or swallowing
- hoarseness
- pale skin
- fast heartbeat
- shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- unexplained weight gain,
- swelling in the abdomen, ankles, feet, or legs
- nausea
- excessive tiredness
- lack of energy
- yellowing of the skin or eyes
- pain in the right upper part of the stomach
- flu-like symptoms
- cloudy, discolored, or bloody urine
- back pain
- difficult or painful urination
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction to meloxicam: sneezing, runny or stuffy nose; wheezing or trouble breathing; hives; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of a heart attack or stroke: chest pain spreading to your jaw or shoulder, sudden numbness or weakness on one side of the body, slurred speech, feeling short of breath.
Stop using meloxicam and call your doctor at once if you have:
- the first sign of any skin rash, no matter how mild;
- shortness of breath (even with mild exertion);
- swelling or rapid weight gain;
- signs of stomach bleeding – bloody or tarry stools, coughing up blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds;
- liver problems – nausea, upper stomach pain, itching, tired feeling, flu-like symptoms, loss of appetite, dark urine, clay-colored stools, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes);
- kidney problems – little or no urinating, painful or difficult urination, swelling in your feet or ankles, feeling tired or short of breath;
- low red blood cells (anemia) – pale skin, feeling light-headed or short of breath, rapid heart rate, trouble concentrating; or
- severe skin reaction – fever, sore throat, swelling in your face or tongue, burning in your eyes, skin pain followed by a red or purple skin rash that spreads (especially in the face or upper body) and causes blistering and peeling.
Meloxicam may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while taking this medication.
Symptoms of overdose may include the following:
- lack of energy
- drowsiness
- nausea
- vomiting
- stomach pain
- bloody, black, or tarry stools
- vomit that is bloody or looks like coffee grounds
- difficulty breathing
- seizures
- coma
- Pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral meloxicam in ruminant calves. Coetzee JF, KuKanich B, Mosher R, Allen PS. Vet Ther. 2009 Winter; 10(4):E1-8.
- COX-1 and COX-2 inhibition in horse blood by phenylbutazone, flunixin, carprofen and meloxicam: an in vitro analysis. Beretta C, Garavaglia G, Cavalli M. Pharmacol Res. 2005 Oct; 52(4):302-6.