What is spotting between periods
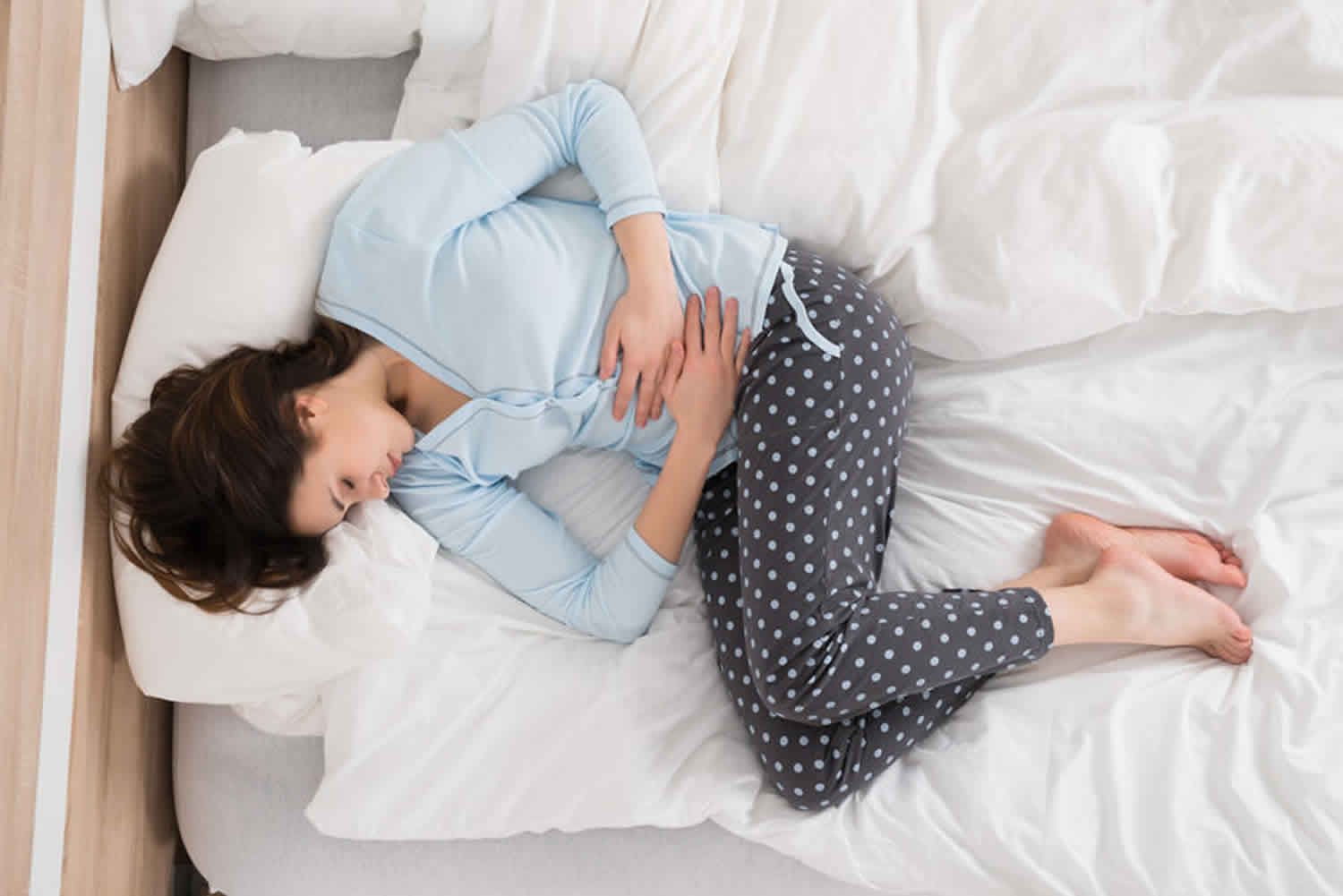
Spotting between periods also called intermenstrual bleeding, is any vaginal bleeding that occurs between a woman’s monthly menstrual periods. Spotting between periods or vaginal bleeding between your periods is not unusual, but should be checked by your doctor if it happens more than once or twice.
There are several things that could cause spotting between periods, such as changes to your hormonal levels, use of hormonal contraception or contraceptive devices, an infection, or an injury, for example.
Spotting between periods should be checked out by your doctor. You should also go to your doctor if you bleed after sex.
Normal menstrual flow lasts about 5 days. It produces a total blood loss of 30 to 80 mL (about 2 to 8 tablespoons), and occurs normally every 21 to 35 days.
Spotting between periods or after menopause can be caused by various problems. Most are benign and can be easily treated. Sometimes, spotting between periods may be due to cancer or pre-cancer. Therefore, any unusual bleeding should be evaluated right away. The risk for cancer increases to about 10% in women with postmenopausal bleeding.
Make sure that bleeding is coming from the vagina and is not from the rectum or the urine. Inserting a tampon into the vagina will confirm the vagina, cervix, or uterus as the source of bleeding.
A careful exam by your doctor is most often the best way to find the source of the bleeding. This exam can be done even while you are bleeding.
You should see your doctor if you have unusual bleeding. This may include:
- Bleeding after sex, more than once
- Spotting or bleeding anytime in the menstrual cycle other than during your period
- Bleeding during your period that is heavier or lasts longer than normal
- Bleeding after menopause
- You are pregnant.
- There is any unexplained bleeding between periods.
- Abnormal bleeding is accompanied by other symptoms, such as pelvic pain, fatigue, dizziness.
What causes spotting between periods
Changes to your hormonal levels
Young women often spot or bleed very slightly when they ovulate (release an egg from the ovary). It happens about 10-14 days after their period and is usually caused by a temporary drop in levels of the hormone estrogen. This is quite normal.
As well as reduced estrogen levels, you may also experience other hormonal imbalances, which are completely harmless. This could be as a result of stress, or a recent change of diet. Your doctor will be able to diagnose this by talking to you, and possibly taking a blood sample, and also advising you about possible treatments.
Girls who have just started their periods and women going through menopause are more likely to have irregular periods.
Use of hormonal contraception
If you have recently started taking hormonal contraceptives it is not uncommon to experience bleeding between periods due to the drop in hormone levels. This will usually happen around two weeks after your last period, and is often referred to as breakthrough bleeding.
Your periods will usually become more regular within six months, and the bleeding between your periods should stop after a month or two. Bleeding between periods can also occur if you forget to take one of your oral contraceptives.
However, if bleeding occurs at other points during your menstrual cycle, you should consult your doctor in order to rule out the possibility of other conditions.
If you have other hormonal contraceptives such as hormone containing intra-uterine devices (IUDs) contraceptive injections or rods you may have some changes to your bleeding pattern. Many women have heavier, longer and more painful periods. This may improve over time.
If you have prolonged bleeding it may be possible for your doctor to give you additional medicine that can help control the bleeding. They may also check the bleeding is not due to other causes such as infection.
Fertility treatments
Vaginal bleeding may occur during certain fertility procedures – for example, during the egg collection stage of IVF treatment. Usually it is mild to moderate bleeding with some cramping. However, if you experience heavy bleeding, you should contact your fertility clinic or doctor for advice.
Other causes
Spotting between periods can also be caused by other conditions including:
- Endometriosis. This condition happens when the lining of the uterus grows outside of the uterus where it does not belong.
- Polyps (growths) in your uterus or cervix
- Inflammation or infection of the cervix (cervicitis)
- Inflammation or infection of the uterus (endometritis)
- Abnormalities in the cervix or uterus
- Uterine fibroids
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Start of a miscarriage
- Other pregnancy complications
- Cancer or pre-cancer of the cervix, uterus, or (very rarely) fallopian tube
- Injury or disease of the vaginal opening (caused by intercourse, trauma, infection, polyp, genital warts, ulcer, or varicose veins)
- IUD use (may cause occasional spotting)
- Vaginal dryness due to lack of estrogen after menopause
- Stress
- Using hormonal birth control irregularly (such as stopping and starting or skipping birth control pills, patches, or estrogen rings)
- Underactive thyroid (low thyroid function)
- Use of blood thinners (anticoagulants)
- Pelvic exam, cervical biopsy, endometrial biopsy, or other procedures
- Ovarian cysts. Unusual bleeding may be a sign of an ovarian cyst that has ruptured (burst).
Spotting between periods diagnosis
Your doctor will perform a physical exam and ask questions about your medical history. The physical exam will include a pelvic exam.
Questions about the bleeding may include:
- When does the bleeding occur and how long does it last?
- How heavy is the bleeding?
- Do you have cramps too?
- Are there things that make the bleeding worse?
- Is there anything that prevents it or relieves it?
- Do you have any other symptoms such as abdominal pain, bruising, pain when urinating, or blood in urine or stools?
Tests that may be done include:
- Blood tests to check thyroid and ovarian function
- Cervical cultures to check for a sexually transmitted infection
- Colposcopy and cervical biopsy
- Endometrial (uterine) biopsy
- Pap smear
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Hysterosonogram
- Hysteroscopy
- Pregnancy test
Spotting between periods treatment
Contact a doctor right away if your spotting between periods is very heavy. Keep track of the number of pads or tampons used over time so that the amount of bleeding can be determined. Uterine blood loss can be estimated by keeping track of how frequently a pad or tampon is soaked and how often one needs to be changed.
If possible, aspirin should be avoided, as it may prolong bleeding. However, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can be used to minimize bleeding and cramping.
Your doctor may start by checking for problems that are most common in your age group. Some of these are not serious and are easy to treat. Your doctor may prescribe hormonal birth control, such as a hormonal IUD, the pill, shot, or vaginal ring, to help control your menstrual cycle. Hormonal birth control is sometimes prescribed by doctors for women’s health concerns other than preventing pregnancy. Other types of bleeding, such as any vaginal bleeding after menopause, can be more serious.