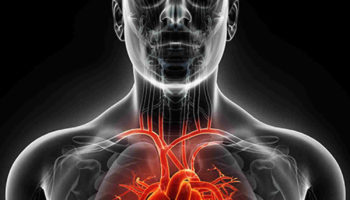
Diastolic dysfunction Diastolic dysfunction also called diastolic heart failure, is heart failure with preserved ejection fraction where the left ventricle loses its ability to relax
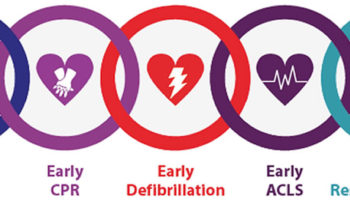
Chain of Survival In 1991, the American Heart Association introduced the “chain of survival” model ((Cummins RO, Ornato JP, Thies WH, Pepe PE. Improving survival
Lymphatic malformation Lymphatic malformation also called macrocystic lymphatic malformation, cystic hygroma or cystic lymphangioma, is a congenital (present at birth) non-cancerous growth that contains one
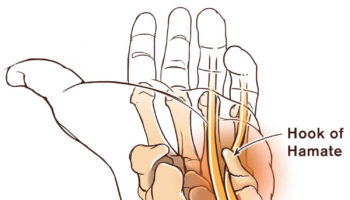
Hamate fracture Hamate fractures can be classified broadly on the basis of the Milch classification into fractures of either the hook or the body. Hamate
Radioulnar synostosis Radioulnar synostosis can take two general forms: congenital radioulnar synostosis and posttraumatic radioulnar synostosis. Each form may be further classified into types. Congenital
Paraphilic disorders The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual fifth edition (DSM-5) definition of paraphilia as "any intense and persistent sexual interest other than sexual interest in
Ganser syndrome Ganser syndrome is a rare and controversial condition, whose main and most striking feature is the production of approximate answers (or near misses)
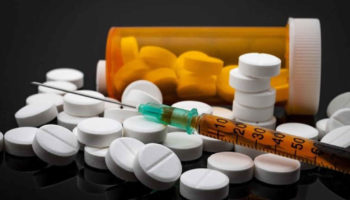
Opioid abuse disorder Opioids, sometimes called narcotics, are a type of drug. Opioids include strong prescription pain relievers, such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, fentanyl, and tramadol.
Cervical strain Cervical strain or cervical neck strain may result from abnormalities in the soft tissues—the muscles, ligaments, and nerves—as well as in bones and
Frostnip Frostnip also known as first-degree frostbite, is a nonfreezing cold injury in which the chilled areas of skin become numb, swollen, and red ((Nonfreezing Tissue Injuries.