What is betaine
Betaine or betaine hydrochloride is a medication that is used to treat high levels of amino acid called homocysteine due to an inherited disorder called homocystinuria (an inherited condition in which the body cannot break down a certain protein, causing build-up of homocysteine in the blood). Increased amounts of homocysteine in the body can cause symptoms such as extreme tiredness, seizures, dislocation of the lens of the eye, abnormal bone structure, osteoporosis (weak bones), blood clots, or decreased weight or rate of weight gain and slowed development in children. Betaine is in a class of medications called nutrients. Betaine works by decreasing the amount of homocysteine in the blood. Betaine is not a cure for homocysteinuria.
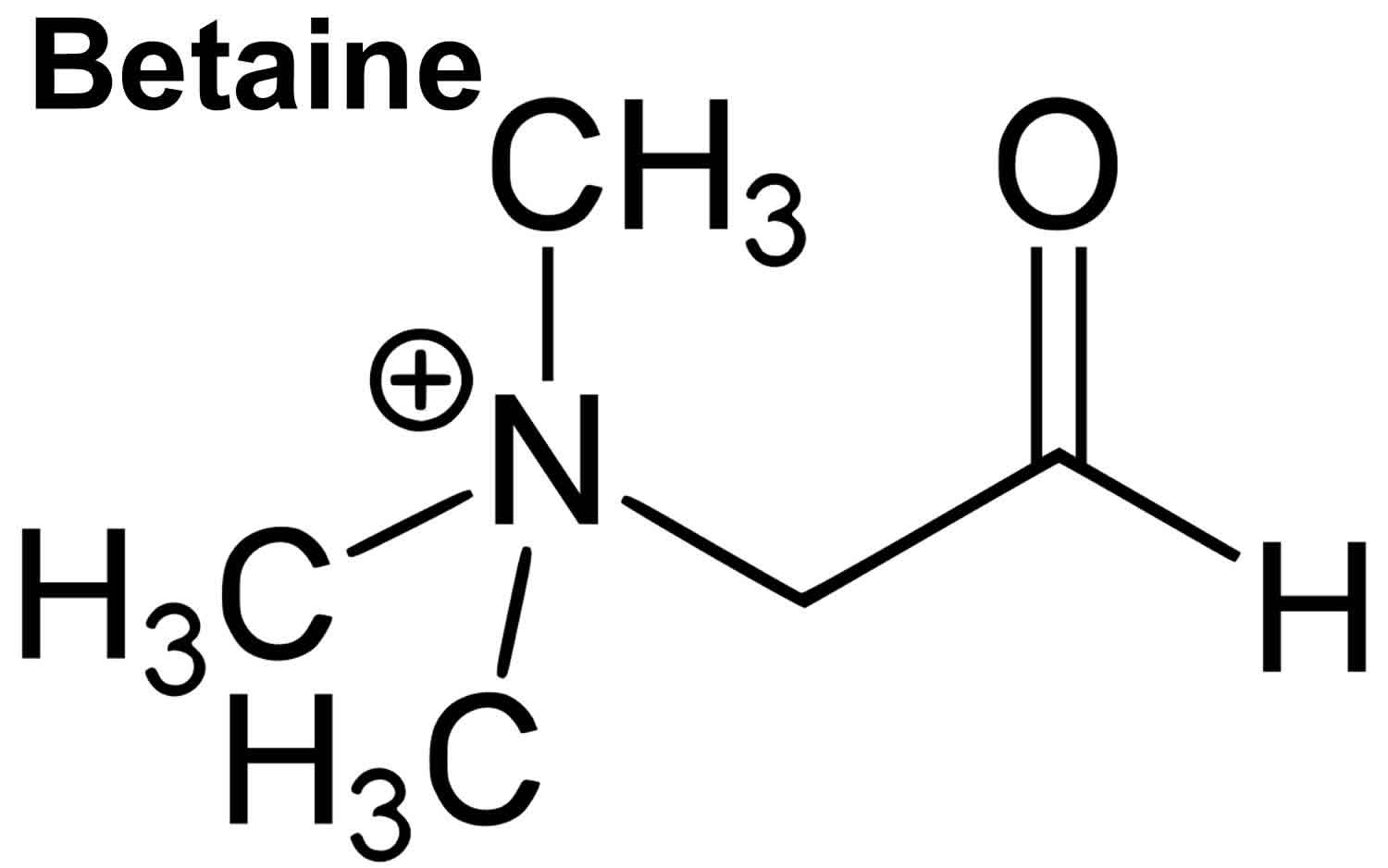
Betaine is a modified amino acid consisting of glycine with three methyl groups that serves as a methyl donor in several metabolic pathways and is used to treat the rare genetic causes of homocystinuria. The homocysteine amino acid can harm blood vessels and contribute to heart disease, stroke, or circulation problems.
Betaine is used to reduce homocysteine levels in people with homocystinuria and by decreasing high homocysteine levels may help prevent serious blood clots, abnormal bone formation, brittle bones (osteoporosis), and eye problems (e.g., dislocated eye lens, nearsightedness).
Laboratory and/or medical tests (e.g., methionine/homocysteine blood levels) may be performed to monitor your progress or check for side effects. Consult your doctor for more details.
Betaine special precautions
Before taking betaine:
- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to betaine or any other medications.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you are taking or plan to take. Your doctor may need to change the doses of your medications or monitor you carefully for side effects.
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had any medical condition.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking betaine, call your doctor.
Be sure to follow all dietary recommendations made by your doctor or dietitian.
How to use betaine
Betaine comes as a powder to be mixed with food or drink and taken by mouth. It is usually taken twice a day or as directed by your doctor. Take betaine at around the same times every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take betaine exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Your doctor will probably start you on a low dose of betaine and gradually increase your dose based on your body’s response to the medication.
Your doctor may tell you to take other medications such as vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), vitamin B12 (cobalamin), and folic acid together with betaine.
Betaine controls homocystinuria but does not cure it. Continue to take betaine even if you feel well. Do not stop taking betaine without talking to your doctor.
To use betaine powder, follow these steps:
- Shake the bottle gently before removing the cap.
- Using the measuring scoop provided, measure the number of scoops your doctor has prescribed. One level scoop of powder is equal to 1 gram of betaine.
- Mix the measured amount of powder with 4 to 6 ounces (120 to 180 milliliters) of water, juice, milk, or formula until the powder is completely dissolved. Betaine powder may also be mixed with food.
- Drink or eat the mixture immediately.
- Replace the cap tightly on the bottle after using.
Dosage is based on your age, weight, medical condition, and response to therapy. Use this medication regularly to get the most benefit from it. To help you remember, take it at the same times each day.
Inform your doctor if your condition persists or worsens.
Betaine HCL dosage
Adult dose for hyperhomocysteinemia
Uses: To decreases elevated blood homocysteine levels in the treatment of homocystinuria from:
- Cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) deficiency
- 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) deficiency
or - Cobalamin cofactor metabolism (cbl) defect
Initial dose: 3 grams orally twice a day
- Increase the dose gradually until plasma total homocysteine is undetectable or only present in small amounts
- Maximum dose: Some patients have required 20 grams/day
Comments:
- One in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic study showed minimal benefit from more than twice daily dosing and 150 mg/kg/day betaine.
- An initial plasma homocysteine response takes several days; steady state is reached within a month.
Pediatric dose for hyperhomocysteinemia
Uses: To decreases elevated blood homocysteine levels in the treatment of homocystinuria from:
- Cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) deficiency
- 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) deficiency
or - Cobalamin cofactor metabolism (cbl) defect
3 years and older:
- Initial dose: 3 grams orally twice a day
- Increase the dose gradually until plasma total homocysteine is undetectable or only present in small amounts
Under 3 years:
- Initial dose: 100 mg/kg/day divided into 2 daily doses
- Increase weekly by 50 mg/kg increments until plasma total homocysteine is undetectable or only present in small amounts
Comments:
- Some patients have required 20 grams/day.
- One in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic study showed minimal benefit from more than twice daily dosing and 150 mg/kg/day betaine.
- An initial plasma homocysteine response takes several days; steady state is reached within a month.
Renal dose adjustments
- Data not available
Dialysis
- Data not available
Liver dose adjustments
- Data not available
What should I do if I forget a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember it. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and continue your regular dosing schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one.
Betaine HCL side effects
Betaine may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if this symptom is severe or does not go away. Nausea, stomach upset, or diarrhea may occur. If any of these effects persist or worsen, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.
Remember that your doctor has prescribed betaine because he or she has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.
Tell your doctor right away if any of these rare but very serious side effects occur:
- persistent headache
- vision changes
- confusion
- drowsiness
- behavior changes
- headache
- vomiting
- seizures
- loss of consciousness
A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, seek immediate medical attention if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including:
- rash
- itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat)
- severe dizziness
- trouble breathing
This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.