Lymph capillaries
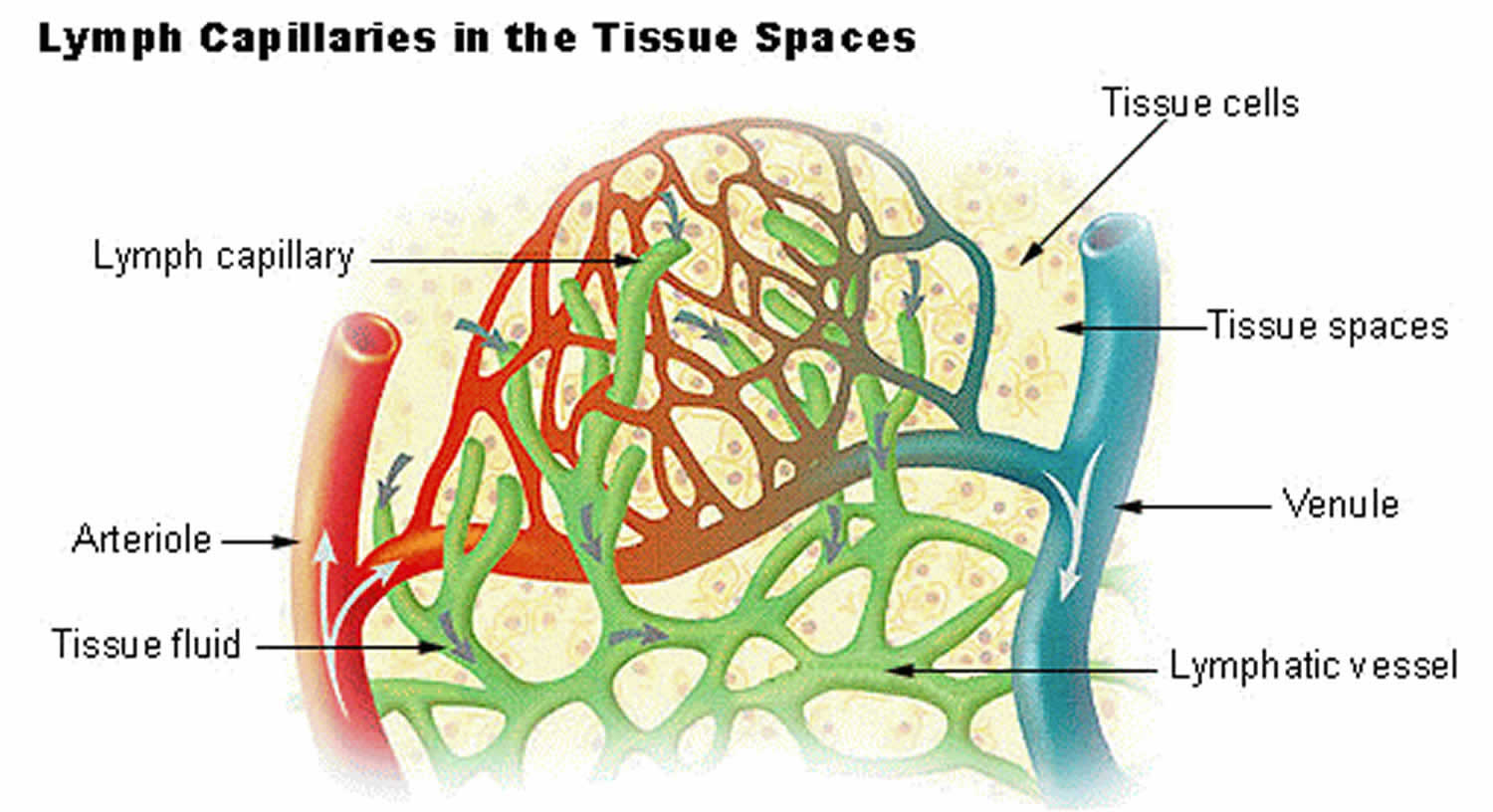
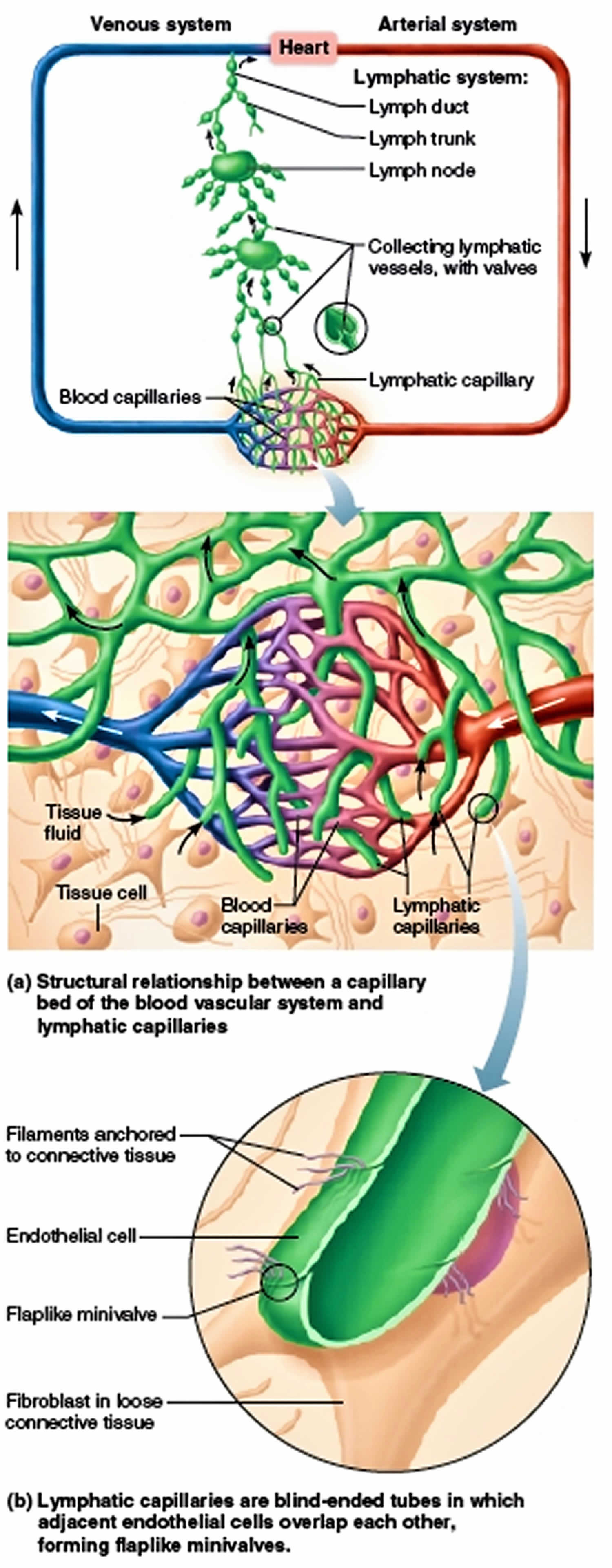
Lymph capillaries also known as lymphatic capillaries, are highly permeable vessels that are closed at one end and are located near blood capillaries in the loose areolar connective tissue throughout the body, except in the central nervous system, and in non-vascular tissues, that collect the excess tissue fluid (Figure 1). Like blood capillaries, lymphatic capillaries wall consists of a single layer of endothelial cells. Lymphatic capillaries permeability results from the structure and arrangement of the endothelial cells. Lymph capillaries have few intercellular junctions, and the edges of adjacent cells overlap, forming easily opened minivalves. Bundles of fine collagen filaments anchor the endothelial cells to the surrounding connective tissue. As a result, any increase in the volume of the tissue fluid separates the minivalve flaps, opening gaps in the wall and allowing the fluid to enter. Once this fluid enters the lymphatic capillaries, it is called lymph. Lymph cannot leak out of the lymphatic capillary because backflow forces the minivalve flaps together.
Although the high permeability of lymphatic capillaries allows the uptake of large quantities of tissue fluid and large protein molecules, it also allows any bacteria, viruses, or cancer cells in the loose connective tissue to enter these capillaries with ease. These pathogenic agents can then travel throughout the body via the lymphatic vessels. However, this threat is averted in part by the lymph nodes, which destroy most pathogens in the lymph.
Lymphatic capillaries are widespread, occurring almost everywhere blood capillaries occur. However, lymphatic capillaries are absent from bone and teeth, from bone marrow, and from the entire central nervous system, where excess tissue fluid drains through the nervous tissue into the cerebrospinal fluid. The cerebrospinal fluid then returns this tissue fluid to the blood at the superior sagittal sinus.
One set of lymphatic capillaries, called lacteals, has a unique function. Located in the villi of the mucosa of the small intestine, lacteals absorb digested fats from the intestine, which causes the lymph draining from the digestive viscera to become milky white (lacte = milk). This fatty lymph is called chyle (juice), and, like all lymph, it is carried to the bloodstream.
Figure 1. Lymphatic capillaries
Lymph capillaries function
Lymphatic capillaries function is to drain excess tissue fluids from around the cell ready to be filtered and returned to the venous circulation. Once inside the lymphatic vessels, this fluid is called lymph (clear water). Any blockage of the lymphatic vessels causes the affected body region to swell with excess tissue fluid, a condition called edema.
From the lymphatic capillaries, lymph enters collecting lymphatic vessels, which accompany blood vessels. In general, the superficial collecting lymphatic vessels in the skin travel with superficial veins, whereas the deep collecting lymphatic vessels of the trunk and digestive viscera travel with the deep arteries. Collecting lymphatic vessels are narrow and delicate, so they usually are not seen in the dissecting laboratory. They have the same tunics as blood vessels (tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa), but their walls are always much thinner. This reflects the fact that lymph flows under very low pressure, because lymphatic vessels are not connected to the pumping heart. To direct the flow of lymph, collecting lymphatic vessels contain more valves than do veins. At the base of each valve, the vessel bulges, forming a pocket in which lymph collects and forces the valve shut. Because of these bulges, each collecting lymphatic vessel resembles a string of beads. This distinctive appearance, which characterizes the larger lymph trunks and lymph ducts as well, allows physicians to recognize lymphatic vessels in X-ray films taken after these vessels are injected with radiopaque dye. This radiographic procedure is called lymphangiography.