What is piezogenic pedal papules
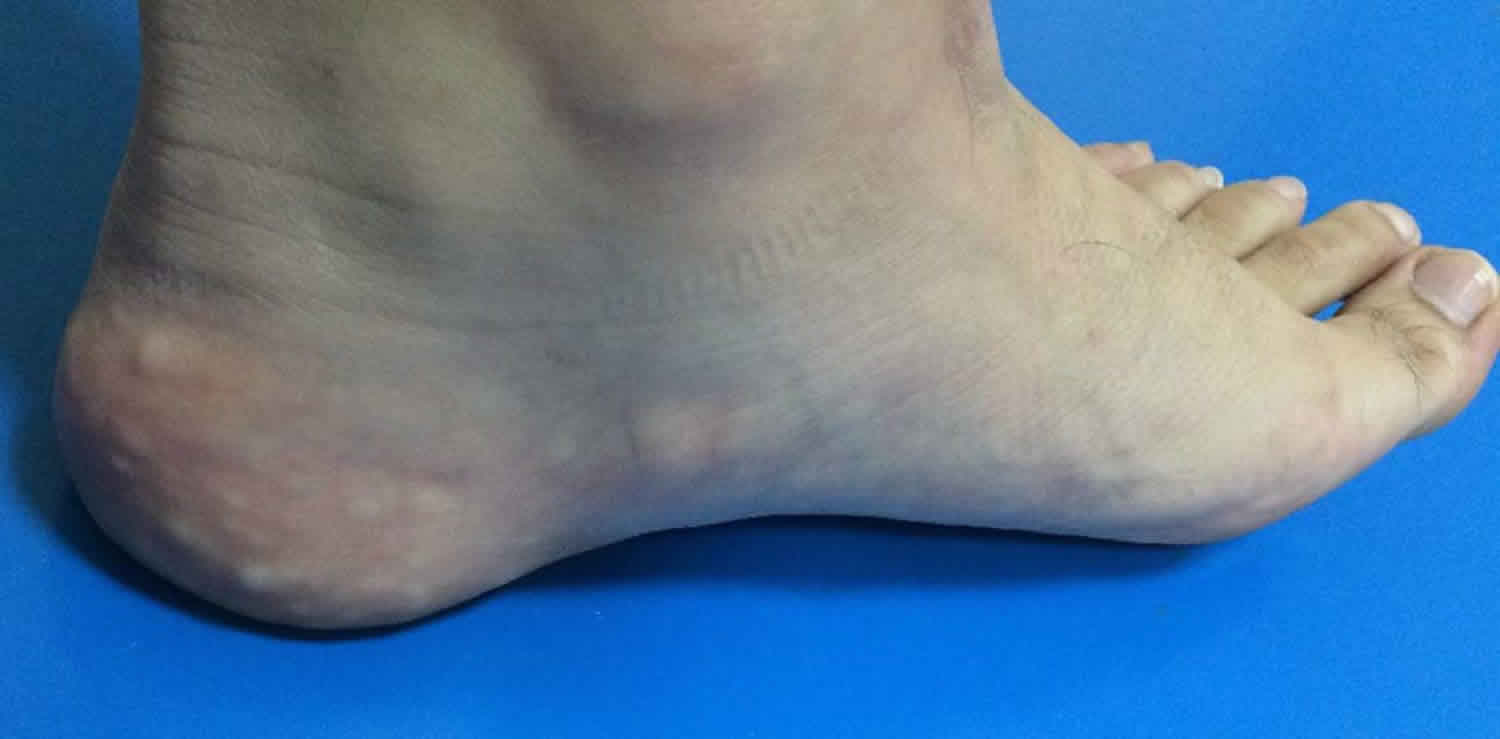
Piezogenic pedal papules or piezogenic papules, are painful or asymptomatic soft, skin-colored papules found on the feet and wrists that result from herniation of fat through the dermis 1. The name “piezogenic” refers to the origin of the papules being pressure. Piezogenic pedal papules are common, nonhereditary, and usually are not the result of an inherent connective tissue defect. Piezogenic pedal papules of the wrist were reported in 1991 2. Piezogenic papules are found in a large number of asymptomatic people. People of all ages, sexes and ethnicities are susceptible to piezogenic papules. They are commonly observed in overweight or obese women. n the United States, 76% of a studied population has been found to have pedal papules; 86% have wrist papules. These occur in all age groups. Piezogenic pedal papules are also associated with underlying connective tissue diseases such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, flat feet, and excessive weight-bearing exercise. Most patients are asymptomatic, although the papules can be painful. Painful papules were found in approximately one third of 29 patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Painful piezogenic papules are also reported to be more frequently in women than in men. Painful papules occur in persons of any age, even children. Infantile pedal papules are seen in 6% of newborns and 40% of infants. Infantile pedal papules differ from adult piezogenic papules. Infantile pedal papules are nodules, occur in the medial plantar aspect of the foot, and lack a piezogenic factor 3.
Do piezogenic pedal papules go away?
No. In most patients, piezogenic pedal papules is of cosmetic concern only. Most patients do not experience pain. However, if lesions become painful, conservative management including behavioral modification, weight loss, avoidance of prolonged standing, and reduced foot trauma should be considered first. Subsequently, compression stockings, heel cups, and orthotics can be used. More invasive techniques should be reserved for refractory cases. Intralesional injections of betamethasone and bupivacaine have been reported with some promise in patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome 4. Lastly, surgical excision may be necessary if lesions are severely painful. A recent case report of successful treatment with deoxycholic acid injection 5.
Piezogenic pedal papules causes
The cause of piezogenic pedal papules is unknown. Piezogenic pedal papules has occurred within families 6, but most cases are believed to be sporadic. Piezogenic papules may be more common in people who are overweight, as well as in individuals with orthopedic problems including flat feet. However, they also can occur in newborns with no clear predisposition. Piezogenic papules may occur more commonly in persons with collagen disorders such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Herniation of fat into the dermis causes the papular appearance. The papules become apparent when an individual stands with full weight on the heels, and they resolve when the weight is removed. The papules, which usually occur bilaterally, may be present on the medial, posterior, and lateral aspects of the heels. Similar papules arise on the volar wrists when pressure is applied.
The histology is similar in both wrist and heel papules, revealing fragmentation of dermal elastic tissue and herniation of subcutaneous fat into the dermis.
Piezogenic pedal papules symptoms
Piezogenic pedal papules are mostly asymptomatic and are noticed incidentally. Occasionally they may be painful.
If the condition is painful, patients may report limitation of occupational or sporting activities.
Piezogenic papules may be more common in people who are overweight, people with flat feet, and people who spend significant time on their feet.
Adult piezogenic pedal papules are more common in women than in men.
Piezogenic pedal papules were seen in 34% of a series of patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, probably resulting from the underlying connective tissue defect.
How are piezogenic pedal papules diagnosed?
Piezogenic pedal papules are usually diagnosed clinically because of the following features:
- Papules resolve when the patient is non-weight bearing
- Papules can usually be compressed
- They mostly occur over posterior and lateral border of the heels
- They are often bilateral
The signs of the condition include herniated papules of fat, usually compressible, mostly in the lateral heels. Examine patients standing with their full weight on the heels. Papules may be present on the medial, posterior, and lateral aspects of the heels. They usually occur bilaterally. The papules are typically 2 mm in diameter.
Papules resolve when the weight is removed. Similar papules may arise on the volar wrists when pressure is applied.
Piezogenic pedal papules treatment
No treatment is required in the absence of symptoms.
For painful lesions, a number of conservative managements have been documented.
- Restriction of weight-bearing exercise
- Weight loss
- Compression stockings
- Foam rubber foot pads, or foam-fitting plastic heel cups
- A consultation with a podiatrist may be helpful.
Intralesional corticosteroid injections have been documented to provide some relief for patients with piezogenic papules with underlying Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Surgical excision may be helpful if symptoms persist despite above managements but this is rarely necessary. Patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome may be at risk for healing complications following surgical intervention. However, in 2004, Doukas et al 7 reported a nonsurgical approach for piezogenic papules. They injected betamethasone and bupivacaine in equal parts (1-2 mL/injection) into an Ehlers-Danlos syndrome patient and reported 50% relief of pain with one injection. Three months later, a second injection yielded a further 20% reduction in pain. After 5 more months, a third injection yielded total relief of pain. At 5-year follow-up, the patient remained asymptomatic.
Piezogenic pedal papules prognosis
In most patients, piezogenic pedal papules is of cosmetic concern only. Painful papules are less common and may correlate with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, obesity, and occupational or sporting exposure. Painful papules can limit participation in sports and may affect occupational activity 8.
References- Piezogenic Pedal Papules. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1081728-overview
- Laing VB, Fleischer AB Jr. Piezogenic wrist papules: a common and asymptomatic finding. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991 Mar. 24(3):415-7.
- Greenberg S, Krafchik BR. Infantile pedal papules. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005 Aug. 53(2):333-4.
- Doukas DJ, Holmes J, Leonard JA. A nonsurgical approach to painful piezogenic pedal papules. Cutis. 2004 May;73(5):339-40, 346.
- Turkmani MG. Piezogenic pedal papules treated successfully with deoxycholic acid injection. JAAD Case Rep. 2018 Jul;4(6):582-583.
- Fangman WL, Prose NS. Precalcaneal congenital fibrolipomatous hamartomas: report of occurrence in half brothers. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004 Nov-Dec. 21(6):655-6.
- Doukas DJ, Holmes J, Leonard JA. A nonsurgical approach to painful piezogenic pedal papules. Cutis. 2004 May. 73(5):339-40, 346.
- Tlougan BE, Mancini AJ, Mandell JA, Cohen DE, Sanchez MR. Skin conditions in figure skaters, ice-hockey players and speed skaters: part I – mechanical dermatoses. Sports Med. 2011 Sep 1. 41(9):709-19.